Saudi Arabia Currency | Riyal (SAR), Exchange Rates, & Money Guide
The Saudi Arabia currency is known as the Saudi riyal. It plays a vital role in the Kingdom’s economic framework. It is abbreviated as SAR. It serves as a medium of exchange and a symbol of the nation’s financial stability and growth.
Understanding the Saudi riyal is essential for both residents and visitors. The riyal reflects the country’s economic journey and integration into the global financial system from historical contexts to modern usage.
Key Facts About the Saudi Riyal (SAR)

The Saudi riyal (SAR) is the official currency of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. This is abbreviated as SAR with the symbol ﷼. It is divided into 100 halalas. Here are some key facts about the Saudi riyal:
- Country: Saudi Arabia
- Currency Code: SAR
- Symbol: ﷼
- Subunit: 1 riyal = 100 halalas
- Coins: 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 halalas
- Banknotes: 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, and 500 riyals
- Central Bank: Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA)
- Exchange Rate: Pegged to the US dollar at a fixed rate of 3.75 SAR to 1 USD
History of the Saudi Riyal
The Saudi riyal has a rich history that reflects the economic development of the KSA(Kingdom of Saudi Arabia). The origins of the riyal, including old coins used before its establishment, can be traced back to the early 20th century. This was when the region transitioned from various local currencies to a unified national currency.
This move was crucial for establishing a stable economic framework as the country was consolidating its territories. This happened under the leadership of King Abdulaziz Al Saud. The adoption of the Saudi riyal marked a significant step in the Kingdom’s journey toward modernization and economic growth.
Historical Exchange Rates
The exchange rates of the Saudi riyal have seen various changes over the years. This reflects both global economic trends and domestic policies. Here is a table summarizing some key historical exchange rates of the Saudi riyal:
|
Year |
Exchange Rate (SAR/USD) |
Notable Events and Changes |
|
1950s |
3.75 |
An initial peg to the US dollar was established. |
|
1960s |
3.75 |
Continued stability and economic growth. |
|
1970s |
3.75 |
Oil boom period with increased revenues. |
|
1980s |
3.75 |
Economic diversification efforts began. |
|
1990s |
3.75 |
Financial reforms and globalization impact. |
|
2000s |
3.75 |
Introduction of Series 5 banknotes with enhanced security. |
|
2010s |
3.75 |
Launch of Vision 2030 and Series 6 banknotes. |
Modern Evolution of the Saudi Riyal
The Saudi riyal has significantly changed its design and security features. These updates reflect the country’s modernization efforts and enhance the currency’s functionality and security.
Series 5
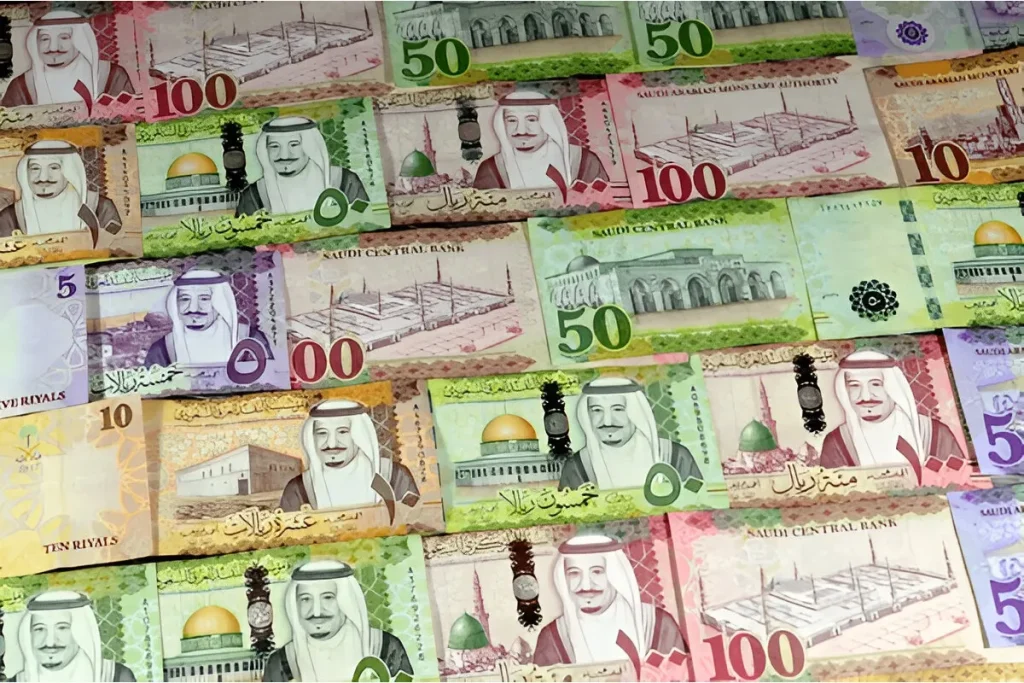

The fifth series of the Saudi riyal was introduced in the 2000s. It marked a pivotal moment in the currency’s evolution. This series featured advanced security measures such as watermarks, holographic strips, and intricate designs to combat counterfeiting.
The banknotes depicted important landmarks and figures in Saudi history. This showcased the Kingdom’s cultural and historical heritage. This series remained in circulation for several years. It laid the groundwork for future enhancements.
|
Denomination |
Obverse Design |
Reverse Design |
Color |
Year of Issue |
|
1 Riyal |
King Abdulaziz Al Saud, 7th century gold dinar coin, and the national emblem |
Palm trees |
Blue |
2007 |
|
5 Riyals |
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz and a traditional Saudi motif |
Desert landscape |
Green |
2007 |
|
10 Riyals |
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz and the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority building |
Oil refinery |
Brown |
2007 |
|
50 Riyals |
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz and the Dome of the Rock |
Al-Masjid al-Nabawi |
Purple |
2007 |
|
100 Riyals |
King Abdullah bin Abdulaziz and the Ministry of Finance building |
Kaaba |
Red |
2007 |
|
500 Riyals |
King Abdulaziz Al Saud and the Kingdom Tower |
Masjid al-Haram |
Blue |
2007 |
Series 6 (2016 series)
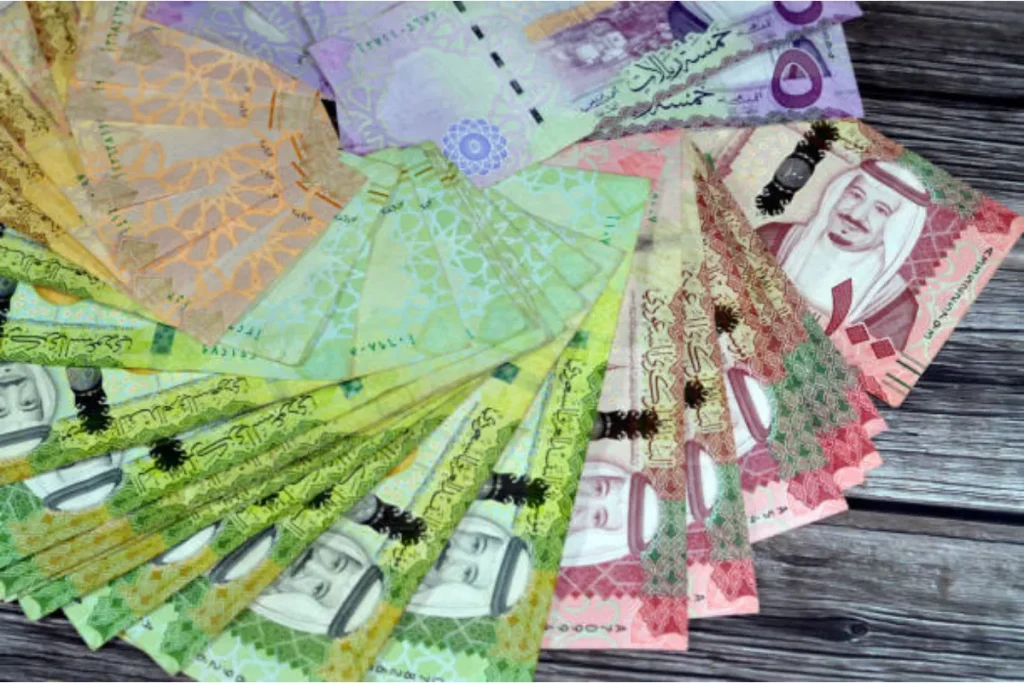

The sixth series of the Saudi riyal was introduced in 2016. It brought more advanced security features and design improvements. These banknotes included tactile elements to assist visually impaired individuals. New materials were used for better durability.
The designs on the banknotes highlighted the Kingdom’s Vision 2030 initiative. This initiative focused on economic diversification and modernization. The introduction of this series showed Saudi Arabia’s dedication to innovation and progress in its monetary system.
|
Denomination |
Obverse Design |
Reverse Design |
Color |
Year of Issue |
|
1 Riyal |
King Salman bin Abdulaziz and the national emblem |
Palm trees |
Blue |
2016 |
|
5 Riyals |
King Salman bin Abdulaziz and an image of the Riyadh skyline |
Desert landscape |
Green |
2016 |
|
10 Riyals |
King Salman bin Abdulaziz and a traditional Saudi motif |
Oil refinery |
Brown |
2016 |
|
50 Riyals |
King Salman bin Abdulaziz and the Dome of the Rock |
Al-Masjid al-Nabawi |
Purple |
2016 |
|
100 Riyals |
King Salman bin Abdulaziz and the Ministry of Finance building |
Kaaba |
Red |
2016 |
|
500 Riyals |
King Salman bin Abdulaziz and the Kingdom Tower |
Masjid al-Haram |
Blue |
2016 |
Recent Trends in Saudi Arabia Currency: An In-Depth Look
The Saudi riyal (SAR) continues to play a crucial role in shaping the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s economic and financial landscape. As the official currency of the country, the riyal has a profound impact on both domestic and international transactions, especially as it is pegged to the US dollar. In this section, we explore recent trends in Saudi Arabia’s currency, its economic shifts, and how it influences both residents and visitors.
Exchange Rate and Currency Stability
The riyal to USD exchange rate remains fixed at 3.75 SAR to 1 USD. This riyal exchange rate has helped maintain stability in the economy, offering predictable exchange rates for money exchange in Saudi Arabia. For example, 1000 riyal to USD is about 266.67 USD, offering convenience for both visitors and businesses.
In recent months, the riyal rate has seen minor fluctuations influenced by global market conditions, particularly the shifting oil prices. Riyadh, the capital city of Saudi Arabia, continues to be a vital economic hub, and fluctuations in the riyal to dollar ratio can affect many aspects of business in the capital, from retail to larger investment opportunities. Riyal to USD has become a key benchmark for international investors to gauge the overall health of the Saudi economy.
Cryptocurrency and the Rise of Digital Riyal
As part of Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, the Kingdom is considering the introduction of digital riyals or e-Riyal, a digital currency aimed at boosting the Kingdom’s financial sector.
This potential shift is significant, as it would allow Saudi riyal (SAR) to interact more seamlessly with global digital currencies, including cryptocurrencies. The digitalization of the riyal could also make it easier for international transactions, aligning with the growing trend of digital money used in global finance.
The introduction of e-Riyal aligns with the global trend of moving toward digital money and providing more secure and faster payment options. As SAR money plays an integral role in global transactions, the adoption of digital currency could provide a smoother path for businesses and individuals.
The Rise of SAR in Crypto
Cryptocurrency is growing in Saudi Arabia. Here’s how:
- Innovation in Finance: Blockchain can make financial services more efficient and secure.
- Digital Riyal (e-Riyal): SAMA is considering a central bank digital currency called “e-Riyal.” This aims to provide a secure way for digital payments.
Saudi Arabia’s focus on blockchain and digital payments is reshaping B2C commerce, enhancing customer transactions
Benefits of Cryptocurrency
Integrating cryptocurrency with the Saudi riyal has several benefits:
- Security: Blockchain offers a secure platform, reducing fraud.
- Speed: Transactions are processed quickly without intermediaries.
- Inclusion: Digital currencies can help unbanked populations access financial services.
The rise of digital currencies is influencing C2C transactions, making peer-to-peer payments more accessible in Saudi Arabia.
Challenges and Regulation
Despite its potential, cryptocurrency faces challenges:
- Regulation: The government is developing rules for cryptocurrency use.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies can be very volatile, posing risks.
Saudi Arabia’s International Trade and Currency Diversification
While Saudi Arabia continues to use the US dollar to riyal peg as the basis for trade and financial exchange, the Kingdom has been exploring methods to diversify its currency exchanges. This includes experimenting with trading in other currencies within Arabian money markets, especially as global oil markets continue to evolve.
The riyal symbol (﷼) remains synonymous with economic stability, yet the Kingdom’s government seeks to minimize its reliance on US dollar to riyal transactions by forging closer ties with other countries.
For example, the 200 SAR to USD conversion rate stands at about 53.33 USD, making SAR attractive for international trade, especially within KSA and neighboring countries. Additionally, the country code for Saudi Arabia is +966, which facilitates direct international dialing for businesses and services involved in cross-border transactions.
The Kingdom’s pursuit of reducing its dependency on the US dollar could reflect the broader economic concept of a fair value gap, where discrepancies arise in asset valuations. As Saudi Arabia explores other trade currencies, this gap could affect the stability of SAR and the future of the riyal.
Saudi Riyal and Economic Challenges
Despite the stability of the riyal to US dollar peg, there are challenges ahead for the Kingdom’s financial system. The rising cost of living, as reflected in the growing population in cities like Riyadh, has pressured local businesses and consumers alike.
A shift in oil prices can influence riyal exchange rate fluctuations, especially affecting imports and exports. The riyal meaning extends beyond just currency—it represents the Kingdom’s efforts to stabilize a shifting global market environment.
As Saudi Arabia explores different economic avenues, it is important to recognize patterns in its financial stability, similar to a double bottom pattern in technical analysis. This pattern often signals a potential reversal or recovery after a period of decline.
Similarly, fluctuations in the riyal and oil prices could follow a similar recovery trajectory, shaping the future economic outlook of the Kingdom.
Saudi Arabia’s Vision for the Future
As Saudi Arabia moves toward a more diversified economy, the role of the riyal will continue to evolve. The Kingdom is committed to ensuring that riyal remains a stable and trusted currency for its population, especially as new sectors emerge beyond oil. The growth of Saudi Arabian money markets, along with increasing digitalization, will likely influence the SAR money flow in the coming years.
For visitors, understanding the 1 USD to riyal conversion rate (approximately 3.75 SAR), as well as how to exchange 100 riyal to USD or 500 riyal to USD, is crucial when planning trips to the capital of Saudi Arabia or other cities. The financial infrastructure in cities like Riyadh offers robust services for both foreign currency exchange and local financial transactions.
Saudi Arabia Currency | Coins and Banknotes

Kingdom of Saudi Arabia currency(KSA money) is available in various denominations. It includes coins and banknotes. Each of them has a unique design and features. These SAR denominations cater to different transaction needs. They also reflect the country’s rich cultural heritage.
Coins
Saudi Arabian coins are also known as halalas. They are used for smaller transactions. The most common denominations include 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 halalas. Each coin features intricate designs that celebrate the Kingdom’s heritage.
The 100 halala coin is equivalent to one riyal. This is often used in day-to-day transactions. The coins are made from durable materials. This ensures they withstand frequent handling and usage.
Banknotes
Saudi Arabia currency banknotes come in several denominations. These include 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, and 500 riyals. Each banknote is distinct in color and design. They showcase important historical figures, landmarks, and cultural symbols.
The 500 riyal note features the portrait of King Abdulaziz Al Saud and an image of the Grand Mosque in Mecca. Advanced security features ensure the authenticity and integrity of the currency.
These features include watermarks and holographic strips. These banknotes(SAR notes) play a crucial role in the country’s economy. They facilitate larger transactions and promote financial stability.
|
Denomination |
Description |
Year of Issue |
|
20 Riyals |
Issued to mark the Saudi Arabian G20 presidency |
2020 |
|
200 Riyals |
Released to commemorate the 200th anniversary of the Kingdom’s founding |
2021 |
The Fixed Exchange Rate System
Saudi Arabia has a fixed exchange rate system. Saudi riyal is pegged to the US dollar at 3.75 SAR to 1 USD. This system provides stability by reducing exchange rate volatility. This is crucial for a country reliant on oil exports.
With a stable exchange rate, Saudi Arabia can manage inflation better. It also creates a predictable environment for international trade and investment.
The fixed exchange rate helps Saudi businesses plan their financial operations with confidence. They know their costs and revenues in foreign currencies will remain stable.
Understanding capital gains tax in California is crucial for investors dealing with foreign currencies like the Saudi riyal.
This predictability is vital for sectors like oil. Oil is priced in US dollars globally. However, the fixed exchange rate system requires the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) to maintain significant foreign currency reserves. This is essential to defend the peg during economic stress or market speculation.
Proposed Monetary Union
The idea of a monetary union in the Gulf region has been discussed for many years. This would involve creating a single currency for the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. These include Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and Oman.
The initiative aims to strengthen economic ties and enhance financial stability in the region. The benefits of a monetary union include easier trade between member countries. It would also reduce transaction costs and improve economic integration.
However, challenges include aligning monetary policies and managing different economic structures. Political consensus is also necessary. At the same time, the proposal remains a topic of discussion. Its implementation requires careful planning and coordination among the GCC countries.
Saudi Riyal and Foreign Exchange

Overview and Macroeconomic Background
Foreign exchange or forex plays a crucial role in Saudi Arabia’s economy. This is heavily dependent on oil revenues. The stability of the Saudi riyal’s exchange rate is vital for maintaining economic health.
The fixed exchange rate system is pegged to the US dollar. This stability ensures that the Saudi Arabia currency system remains predictable, supporting international trade and effectively managing inflation. The probability of default plays a key role in maintaining the stability of pegged currencies like the Saudi riyal.
Governance and Speculation
The Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority (SAMA) oversees the country’s foreign exchange market. It ensures the stability of the riyal through effective governance and regulatory measures.
Economic data, political events, and market sentiment can influence speculation in the forex market. SAMA monitors these factors closely to mitigate risks and maintain currency stability.
Intervention Tactics and Domestic Implications
SAMA employs various tactics to intervene in the foreign exchange market. It includes adjusting interest rates, using foreign currency reserves, and implementing regulatory measures.
These interventions help curb excessive speculation and maintain the fixed exchange rate. Managing speculation is crucial for protecting the purchasing power of Saudi citizens and maintaining economic stability.
Practical Aspects of Saudi Currency and Payments
Understanding the practical aspects of using Saudi currency is essential for anyone. Engaging with the Kingdom’s economy is crucial for both visitors and residents.
The Basics of Saudi Currency
What is a Saudi Riyal? The Saudi riyal abbreviation is SAR. It is the official currency of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia(Riyal KSA). It is divided into 100 halalas.
It is available in various denominations of coins and banknotes. The riyal’s stability is maintained through its fixed exchange rate with the US dollar.
Credit Card Usage and Cash Needs
Credit cards are widely accepted in Saudi Arabia, especially in Riyadh and Jeddah(urban areas). However, it is advisable to carry some cash for smaller transactions.
There are more remote areas where card payments might not be as common. Consider the daily expenses before planning your trip. You must be sure that you have sufficient SAR money to cover these.
Sending and Receiving Money
Sending and receiving money in Saudi Arabia is relatively straightforward. There are numerous banks and money transfer services available.
International transfers can be made through various financial institutions. However, the Local transfers are facilitated by the extensive banking network within the Kingdom.
Taxes and Financial Preparation
Saudi Arabia has implemented a Value-Added Tax(VAT) on goods and services. It is important to be aware of this when making purchases. Understanding the tax structure will help you manage your finances.
This helps you more effectively during your stay. Proper financial preparation ensures a smooth experience when dealing with Saudi currency and payments.
The Saudi Arabian riyal symbolizes the Kingdom’s economic stability and growth. By exploring its history, modern features, and practical uses, you can gain valuable insights into its significance.
Whether you’re a visitor, a business professional, or a currency enthusiast, understanding the riyal helps you navigate financial transactions in Saudi Arabia with confidence.
FAQ’s
How much is $100 US in Saudi?
The exchange rate between the US dollar and the Saudi Riyal can vary, but as of now, 100 US dollars is approximately equivalent to 375 Saudi Riyals. It's always a good idea to check the current exchange rate for the most accurate conversion.
What is the symbol of SAR?
The symbol for the Saudi Riyal is "ر.س" in Arabic or "SAR" in English. This symbol is used to represent the currency in financial transactions and other monetary contexts.
What is Saudi dinar?
There is no Saudi dinar. Saudi Arabia's official currency is the Saudi Riyal (SAR). The term "dinar" is used in other Middle Eastern countries, such as Kuwait and Bahrain, but not in Saudi Arabia.
How many countries use riyal?
The riyal is used as the official currency in three countries: Saudi Arabia (Saudi Riyal), Yemen (Yemeni Riyal), and Qatar (Qatari Riyal). Each of these countries has its version of the riyal.