Understanding PMB Meaning | Key Definitions, Benefits, and Applications
Managing projects, securing healthcare benefits, or handling mail can be overwhelming. Many people struggle with ensuring they’re using the right tools for tracking project performance, getting the necessary healthcare coverage, or receiving mail securely.
Understanding the PMB meaning can simplify these challenges. Whether it’s a Performance Measurement Baseline in project management, Prescribed Minimum Benefits in healthcare, or a Private Mailbox for secure mail handling, PMB provides solutions to common problems in these areas.
Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) in Project Management
What is a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB)?
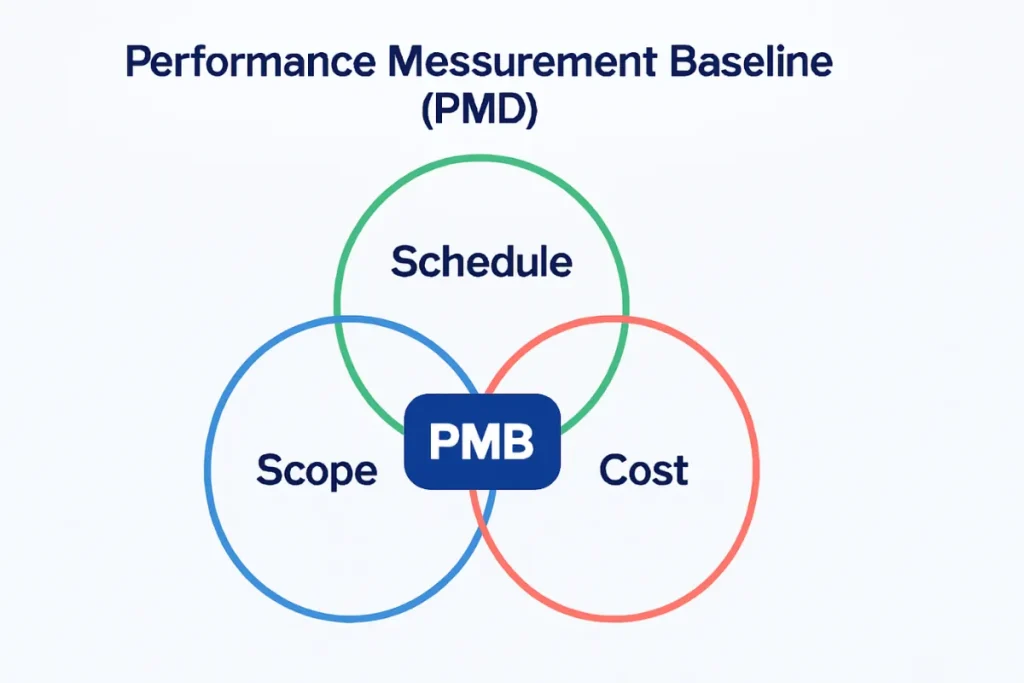
In project management, PMB meaning refers to the Performance Measurement Baseline, an essential component for tracking and managing the performance of a project. It is the approved version of a project plan, which integrates the scope, schedule, and cost baselines.
This baseline serves as a benchmark for measuring the project’s progress and performance. By setting clear parameters for scope, time, and budget, PMB helps project managers and stakeholders keep track of how the project is performing against the initial goals. Understanding PMB helps in financial planning, much like Capital Gains Tax considerations.
Purpose of PMB in Project Management
The primary purpose of the Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) is to provide a standard for measuring and evaluating the progress of a project. It acts as a reference point that helps project managers identify variances in scope, schedule, and cost.
If the project deviates from the baseline, corrective actions can be taken to get the project back on track. This allows managers to monitor progress and control the project efficiently, ensuring that resources are used effectively and that the project stays within budget and time constraints. Performance Management relies on tools like PMB to track and evaluate project success.
Key Components of PMB
The PMB is divided into three major baselines that contribute to its overall success:
- Scope Baseline: This defines the project’s deliverables and the work required to achieve them. It helps prevent scope creep by ensuring the project’s goals are clearly outlined and agreed upon.
- Schedule Baseline: This sets the timeline for completing the project and its various components. It helps to identify milestones and deadlines that need to be met.
- Cost Baseline: This defines the budget for the project, including the estimated costs of resources, labor, and materials. It ensures the project is completed within its financial constraints.
Together, these baselines allow the project team to assess performance, track milestones, and manage changes effectively throughout the project’s lifecycle.
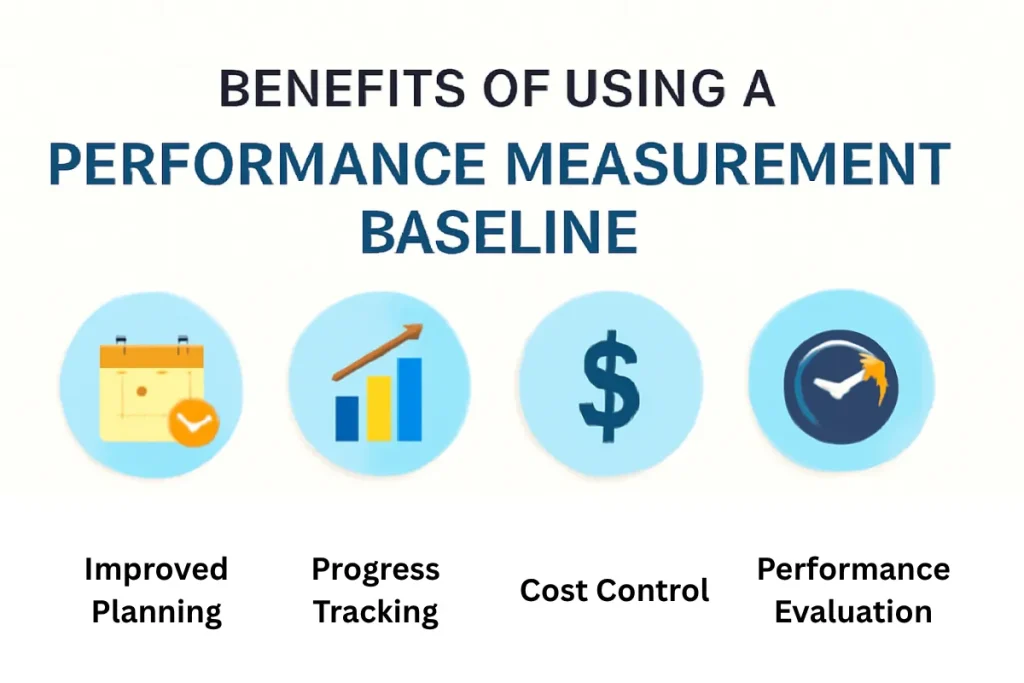
Benefits of Using a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB)
Tracking Project Performance with PMB
One of the key benefits of using a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) is its ability to track the progress and performance of a project over time. By comparing the actual performance to the approved baseline, project managers can easily spot any discrepancies.
This allows for early identification of issues such as delays or budget overruns, enabling corrective actions to be implemented promptly. With a clear reference point, PMB ensures that the project stays on course and meets its objectives. Like data validation, PMB ensures accurate tracking of project progress.
Why PMB is Critical for Project Success
PMB plays a crucial role in ensuring project success by providing a clear and standardized way to measure performance. It helps in making informed decisions by offering accurate data on the project’s status. With PMB, project managers can monitor the use of resources, check the alignment of project goals, and verify that timelines are being adhered to.
Furthermore, it increases accountability by setting clear expectations for the entire team. When everyone is aware of the baseline, there is a mutual understanding of what needs to be achieved and by when. This clarity helps minimize risks and improves the likelihood of completing the project successfully, on time, and within budget.
PMB and Improved Decision-Making
The Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) also enhances decision-making processes. By continuously monitoring the project against the baseline, project managers can assess whether corrective actions are needed.
Whether it’s reallocating resources, adjusting the schedule, or revising the budget, PMB provides the data necessary to make these decisions in real time. This leads to better management of project risks, improved resource allocation, and ultimately, a more successful project outcome.
How to Create and Use a Performance Measurement Baseline
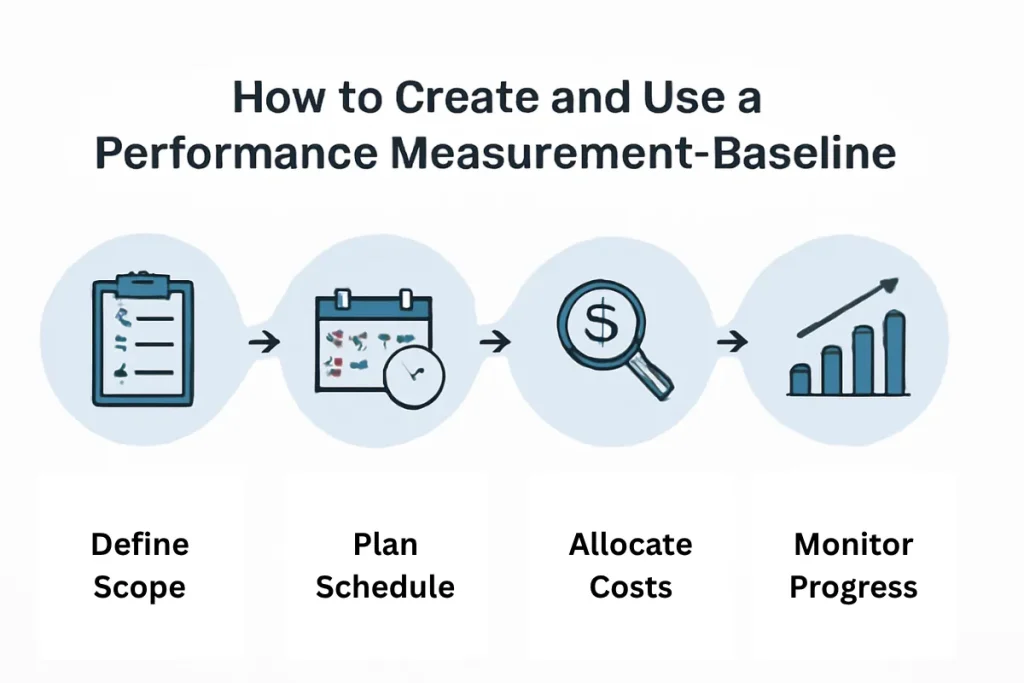
Steps to Establish a PMB
Creating a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) involves several steps that require careful planning and input from various project stakeholders. Here’s a simplified process to establish your PMB:
- Define Project Scope: Begin by clearly outlining the deliverables and boundaries of the project. This includes identifying the key objectives, tasks, and milestones. Ensuring everyone has a shared understanding of the scope helps prevent scope creep.
- Set the Schedule: Develop a detailed timeline, specifying when each task will start and finish. Break the project into smaller phases or milestones, with specific deadlines for each. It’s essential to identify dependencies between tasks and ensure the schedule is realistic.
- Estimate Costs: Create a budget by estimating the costs associated with each phase or task. This involves considering the labor, materials, equipment, and other resources required. Set a maximum budget for each task to ensure financial control.
- Integrate the Baselines: Combine the scope, schedule, and cost baselines into a single PMB. This creates a comprehensive project plan that outlines not just the deliverables, but also the timing and costs associated with each one.
- Get Approval: Once the PMB is created, it must be reviewed and approved by key stakeholders, including project sponsors and team members. Approval ensures that everyone is aligned on the project’s objectives, schedule, and costs.
Tools and Techniques for Creating PMB
To efficiently create and manage a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB), project managers can utilize various tools and techniques:
- Project Management Software: Tools like Microsoft Project, Trello, or Asana help in defining and tracking project baselines, managing tasks, and setting timelines.
- Earned Value Management (EVM): This technique integrates cost, schedule, and scope baselines, helping to monitor project performance and forecast future trends.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): A WBS helps break down the scope into smaller, manageable tasks, ensuring all deliverables are captured and included in the PMB.
Using these tools ensures that the PMB is comprehensive, well-organized, and easy to track, making the process of managing a project much more streamlined. Data verification is crucial, just like ensuring a correct PMB during project setup.
PMB and Earned Value Management (EVM)
Once the Performance Measurement Baseline is in place, it can be effectively used in conjunction with Earned Value Management (EVM) to track project performance. EVM is a powerful method that compares the planned progress with the actual progress to assess whether the project is on track.
By measuring the value of the work completed, EVM provides insights into how much money and time have been used versus what was planned. Integrating PMB with EVM provides an accurate and real-time view of the project’s health, enabling managers to make data-driven decisions. It highlights potential delays, cost overruns, or scope changes early, allowing corrective measures to be taken quickly.
Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMB) in Healthcare
What Are Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMBs)?
In the context of healthcare, PMB meaning refers to Prescribed Minimum Benefits, which are defined sets of healthcare services that medical schemes must cover for all their members, regardless of the plan. These benefits are mandated by law to ensure that everyone has access to essential health services, even those with the most basic or limited health insurance plans.
Prescribed Minimum Benefits typically include life-threatening emergencies, chronic conditions, and conditions that are expensive to treat but necessary for long-term well-being. In some countries, such as South Africa, these benefits are regulated by health authorities to maintain equity in healthcare access.
Just as channel marketing focuses on ensuring that businesses communicate and distribute effectively through the right channels, PMBs ensure that essential medical services are effectively provided to all members, regardless of their health plan. PMBs ensure essential healthcare services, similar to how channel marketing ensures proper distribution.
Importance of PMB in Medical Schemes
PMBs are important because they ensure that all members, regardless of their specific medical plan, have access to a standard level of healthcare coverage. Without PMBs, individuals in basic medical schemes may be left without coverage for essential healthcare services, leading to significant health disparities.
By requiring the inclusion of these benefits, PMBs help to improve overall public health, provide peace of mind, and promote a healthier society. For medical schemes, PMBs help in ensuring that their members are protected from the high cost of serious illnesses. In addition, they assist in managing healthcare expenses by setting clear guidelines on the minimum benefits that must be provided.
In healthcare, understanding Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMB) is as crucial as conducting a site survey for a project. Just as a site survey helps gather data before starting construction, PMBs define the essential services that need to be provided under any medical scheme. Much like a site survey, PMBs define essential services in healthcare.
Types of Services Covered by Prescribed Minimum Benefits
PMBs typically cover a range of healthcare services, ensuring that all individuals have access to necessary treatments regardless of their plan. The types of services included in PMBs often involve:
- Emergency Medical Services: Life-threatening emergencies must be covered under PMB, ensuring that individuals receive immediate care in critical situations.
- Chronic Disease Management: Medical schemes must provide coverage for the long-term treatment of chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma.
- Hospitalization: Basic hospital services, including treatment for conditions that require hospitalization, must be covered by PMB.
- Specialized Treatment: Certain specialized treatments, such as cancer care or surgeries, are also typically included in PMB coverage, ensuring equitable access to necessary healthcare.
These services are vital for preventing the financial burden on individuals and ensuring they have access to life-saving treatments, regardless of their healthcare plan.
Benefits of Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMB)

PMBs offer several key benefits to both individuals and healthcare systems:
- Improved Access to Care: PMBs ensure that essential healthcare services are available to everyone, promoting equality in healthcare access and helping those with limited resources.
- Cost Control: By defining the minimum benefits required, PMBs help control the cost of healthcare by setting boundaries on the coverage that must be provided.
- Better Health Outcomes: With access to necessary treatments and interventions, PMBs contribute to improved health outcomes for individuals, particularly those with chronic conditions or emergency medical needs.
- Legal Protection for Members: PMBs provide a layer of legal protection for individuals by ensuring that their medical schemes must cover essential services, regardless of the specific plan they are enrolled in.
Overall, PMBs are crucial for ensuring a baseline level of healthcare that supports public health, reduces disparities, and helps individuals manage serious health conditions. By having these benefits guaranteed by law, members of medical schemes are assured of receiving essential care, which enhances their quality of life.
Private Mailbox (PMB): A Secure Alternative to PO Box
What is a Private Mailbox?

A Private Mailbox (PMB), often referred to as a virtual address, is a service that provides individuals or businesses with a real street address instead of a traditional PO Box.
The main difference between a PO Box and a Private Mailbox is that the latter is not just a box within a post office; it offers a complete street address, which can be used for receiving mail and packages from all couriers, not just the postal service.
This makes it an attractive option for people who want to maintain privacy, enhance their professional image, or have access to a broader range of mail services. A Private Mailbox can be particularly useful for businesses, freelancers, and digital nomads who need a stable, professional address for their correspondence.
Unlike a PO Box, which only accepts mail delivered by the USPS, a PMB allows for mail forwarding and package acceptance from various couriers like UPS and FedEx. A Private Mailbox can enhance the image of businesses in high-ticket sales.
Advantages of Using a Private Mailbox
- Real Street Address: One of the key benefits of a Private Mailbox is that it offers a real street address, which can be used for business correspondence and even as your official mailing address. This makes it an ideal solution for businesses looking to maintain a professional image while keeping their home address private.
- Privacy and Security: With a Private Mailbox, you can avoid using your home address for receiving personal or business mail. This adds an extra layer of privacy and security, especially for individuals concerned about identity theft or businesses wanting to separate personal and professional matters.
- Mail Forwarding: Private mailbox services typically offer mail forwarding capabilities, allowing you to receive mail at your PMB and have it forwarded to any location you choose. This feature is especially useful for individuals who travel frequently or have businesses in multiple locations.
- Package Acceptance: Unlike PO Boxes, a Private Mailbox allows you to receive packages from all courier services. This means you can accept deliveries from UPS, FedEx, DHL, and other companies, offering more flexibility compared to a P.O. Box.
- Flexibility for Businesses: For businesses, having a Private Mailbox provides a professional image, as it’s often associated with a commercial address. It allows businesses to keep their residential address confidential, preventing potential customers from accessing personal details.
When to Choose a Private Mailbox Over a P.O. Box
Choosing between a Private Mailbox and a P.O. Box depends on your needs. If you require a real street address for receiving mail and packages from various couriers, a Private Mailbox is the ideal choice. Here are a few reasons you might prefer a PMB over a PO Box:
- Business Use: If you run a business, a PMB offers the professional street address that customers can use to contact you. This is crucial for businesses wanting to maintain a professional image and for those who need to receive packages from different delivery services.
- Privacy Concerns: If you value privacy and want to keep your home address confidential, a PMB ensures that you are not using your address for receiving mail or packages. It’s an excellent option for individuals concerned about their privacy, especially for entrepreneurs and freelancers.
- Frequent Travelers: If you travel often or live in different locations, a Private Mailbox can be a convenient option. It provides a mail forwarding service, which ensures you never miss important mail, regardless of where you are.
While PO Boxes are suitable for some individuals, a Private Mailbox offers far more benefits, especially for those requiring additional services such as mail forwarding, accepting packages, or maintaining a professional address.
Is a Private Mailbox Necessary Over PO Box Rental?
Private Mailbox vs PO Box: Which is Better?
When deciding between a Private Mailbox (PMB) and a PO Box, it’s important to understand the key differences in functionality, privacy, and convenience. A PO Box is a simple and cost-effective option for those who need a basic mailing address through the USPS. However, a Private Mailbox offers more flexibility and a range of features that a PO Box does not.
- Real Street Address: One of the most significant advantages of a Private Mailbox is that it provides a real street address. This is especially beneficial for businesses and individuals who want to project a professional image or require a physical location for their mail. A PO Box, on the other hand, only provides a post office box number, limiting its use for certain types of mail, particularly packages delivered by other carriers like UPS or FedEx.
- Package Acceptance: Unlike PO Boxes, which only accept mail through the USPS, a Private Mailbox can receive packages from all delivery services, including UPS, FedEx, and DHL. This makes it a much more versatile option for individuals and businesses that regularly receive parcels.
- Mail Forwarding: Private Mailbox services often include mail forwarding, allowing you to have your mail and packages sent to any address you choose. This is particularly useful for people who travel frequently or those living in different locations. PO Boxes generally do not provide mail forwarding services, making them less flexible for those who need mail forwarded to a different address.
- Enhanced Privacy: A Private Mailbox also provides enhanced privacy compared to a PO Box. With a Private Mailbox, your home address stays private, and your business or personal mail is handled securely. If you use a PO Box, it may not offer the same level of security or discretion, as it is more commonly used by people with less concern for maintaining privacy.
Why a Private Mailbox May Be the Better Choice
For individuals and businesses that require more than just a simple address, a Private Mailbox offers several advantages that make it a more appealing choice over a PO Box rental. Here are some specific scenarios where choosing a Private Mailbox would be beneficial:
- For Businesses: A Private Mailbox offers the professional street address that businesses need to maintain credibility and legitimacy. It allows for mail from all couriers, and it keeps your business operations private, with no need to disclose your residential address.
- For Frequent Travelers: A Private Mailbox is a great solution for those who travel often. With mail forwarding, you can receive important documents and packages regardless of where you are. This is especially important for people who work remotely or are constantly on the move.
- For Enhanced Privacy: If privacy is a top concern, a Private Mailbox offers the added security of a real street address, ensuring your address is never exposed. This is particularly useful for individuals who are concerned about identity theft or need to separate their personal and business mail.
- For Secure Package Handling: If you frequently receive packages, a Private Mailbox is a much better option. It accepts packages from all delivery services, unlike a PO Box, which limits deliveries to the USPS only.
While PO Box rentals are generally more affordable, a Private Mailbox offers more features, security, and flexibility, making it a better choice for those who require a professional address, need to receive packages from all delivery services, or want to ensure greater privacy and mail handling convenience.
What is the Difference Between a PO Box and a Private Mailbox?
PO Box Overview
A PO Box (Post Office Box) is a service provided by the USPS that allows individuals or businesses to rent a box at a local post office to receive mail.
The primary purpose of a PO Box is to offer a secure and private place for receiving mail, especially for those who do not have a permanent or reliable mailing address. It is commonly used by people who may not want to use their home address for receiving personal or business-related correspondence.
However, a PO Box comes with certain limitations. It only accepts mail that is delivered through the USPS, meaning it cannot be used to receive packages from other couriers like UPS, FedEx, or DHL. Additionally, while it provides a level of privacy, it does not offer the flexibility or services that a Private Mailbox does.
Private Mailbox (PMB) Overview
A Private Mailbox (PMB), in contrast, offers a real street address rather than just a post office box number. This street address can be used for receiving mail and packages from all major courier services, including UPS, FedEx, and DHL.
A Private Mailbox is typically offered by private companies or mail centers, and it provides more flexibility and a higher level of service than a standard PO Box.
In addition to receiving all types of mail and packages, Private Mailbox services often include features like mail forwarding, where your mail can be sent to any location of your choice, and 24/7 access, allowing you to pick up your mail at any time, depending on the service provider.
Key Differences Between PO Box and Private Mailbox
- Address Type:
- PO Box: A PO Box gives you a post office box number that can only be used for receiving USPS mail.
- Private Mailbox: A PMB provides you with a real street address, which can be used for receiving mail and packages from all courier services.
- PO Box: A PO Box gives you a post office box number that can only be used for receiving USPS mail.
- Mail Delivery:
- PO Box: Only accepts mail delivered by USPS, making it less versatile for those who need to receive packages from other courier services.
- Private Mailbox: Accepts mail from USPS, UPS, FedEx, DHL, and other delivery services, providing a wider range of mail handling options.
- PO Box: Only accepts mail delivered by USPS, making it less versatile for those who need to receive packages from other courier services.
- Privacy:
- PO Box: A PO Box provides some level of privacy since your home address is not exposed. However, it does not offer the same level of security or professional appearance as a PMB.
- Private Mailbox: A PMB offers greater privacy, as it provides a real street address that can be used for both personal and business purposes. It also offers secure mail handling and privacy protection.
- PO Box: A PO Box provides some level of privacy since your home address is not exposed. However, it does not offer the same level of security or professional appearance as a PMB.
- Additional Services:
- PO Box: Basic service for receiving mail, with limited additional features.
- Private Mailbox: Many PMB providers offer extra services like mail forwarding, package acceptance, secure mail storage, and 24/7 access, which are not available with a standard PO Box.
- PO Box: Basic service for receiving mail, with limited additional features.
Why Choose a Private Mailbox Over a PO Box?
A Private Mailbox (PMB) is often the better option for individuals and businesses that require flexibility, privacy, and enhanced services. Here are a few reasons why you might choose a Private Mailbox over a PO Box:
- Business Use: A Private Mailbox provides a professional street address that is essential for businesses. It gives your company credibility and ensures that your clients and customers can send packages or documents to a real address, not just a post office box number.
- Frequent Package Receiving: If you regularly receive packages from services like UPS or FedEx, a Private Mailbox is the obvious choice, as it accepts packages from all major delivery companies.
- Travelers and Remote Workers: If you travel frequently or work remotely, a Private Mailbox provides the convenience of mail forwarding, ensuring you can receive important documents from anywhere.
- Better Privacy and Security: With a Private Mailbox, you can keep your address confidential while having a secure and reliable way to receive mail and packages.
How to Address a PO Box and Private Mailbox
PO Box Address Format
When addressing mail to a PO Box, it is important to use the correct format to ensure that the mail is delivered properly. Here’s how to properly address an envelope or package to a PO Box:
- Recipient’s Name
- PO Box Number
- City, State, ZIP Code
Example:
John Doe
PO Box 1234
Los Angeles, CA 90001It’s crucial to note that PO Box addresses are specific to the post office, and mail can only be delivered by the USPS. This format ensures the mail is directed to the right location within the post office where the PO Box is assigned.
Private Mailbox Address Format
Addressing a Private Mailbox (PMB) is slightly different because it involves using a real street address instead of a post office box number. The Private Mailbox provides the flexibility of receiving mail and packages from all couriers, and the address format reflects this. Here’s how you should address mail to a Private Mailbox:
- Recipient’s Name
- Private Mailbox Number (PMB)
- Street Address of Mailbox Provider
- City, State, ZIP Code
Example:
John Doe
PMB 1234
123 Main Street
Los Angeles, CA 90001In this format, the Private Mailbox number (PMB) replaces the PO Box number, and the street address of the mailbox provider is included. This allows the mail to be processed and handled by the Private Mailbox service provider, which can forward it to the recipient or hold it for pickup.
How to Address a Letter to a PO Box
When addressing a letter to a PO Box, ensure that you place the PO Box number in the correct field, followed by the appropriate city, state, and ZIP code. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Recipient Name: The person or business you are sending the letter to.
- PO Box Number: Clearly state the PO Box number.
- City, State, and ZIP Code: Make sure to include the correct postal code to ensure delivery.
While this format works well for sending mail through the USPS, it does not accept packages from couriers like UPS or FedEx.
How to Address a Letter to a Private Mailbox
When addressing a letter to a Private Mailbox, ensure that you follow the format that includes the PMB number and the street address of the mailbox provider. This format is essential for receiving both regular mail and packages from multiple couriers:
- Recipient Name: The intended recipient.
- PMB Number: The Private Mailbox number assigned by the service provider.
- Street Address: The mailbox provider’s street address (not a post office address).
- City, State, and ZIP Code: Complete postal information.
For example, if you have a Private Mailbox through a service like The UPS Store, the format would look like this:
John Doe
PMB 1234
456 Business Blvd.
Los Angeles, CA 90001This format ensures that the mail is directed to the correct location and can be accepted by all major carriers, making it a more versatile option compared to a PO Box.
Mail Forwarding and Suite Number
For both PO Boxes and Private Mailboxes, some providers may offer mail forwarding services, allowing you to forward your mail to a different address if needed. If you have a Private Mailbox, you may also include a suite number (if provided) in the address for mail handling. This ensures that your mail is correctly routed to the appropriate suite within the mail provider’s facility.
Real-World Applications of PMB (Performance Measurement Baseline, Private Mailbox, and Prescribed Minimum Benefits)
PMB in Project Management
The Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) is a vital tool in project management that helps project managers track the progress of a project, ensure resources are used efficiently, and keep the project within scope, schedule, and budget. PMB is particularly useful in large-scale projects, where managing various elements simultaneously can be challenging.
Real-World Example: Consider a construction company that is building a commercial property. The company sets a Performance Measurement Baseline that includes the scope of the building (size, layout), the schedule (expected completion dates for each phase), and the costs (materials, labor, permits). As the project progresses, the project manager uses the PMB to compare the actual progress against the baseline. If there’s a delay in construction or an unexpected increase in costs, the manager can identify the issue early and make adjustments to get the project back on track.
By consistently comparing the Performance Measurement Baseline with real-time data, project managers can ensure projects meet deadlines, stay within budget, and maintain quality standards.
Private Mailbox in Business and Personal Use
Private Mailboxes (PMB) are increasingly being used by both individuals and businesses for various reasons, ranging from privacy to convenience. A Private Mailbox provides a real street address, making it more professional and versatile than a PO Box.
Real-World Example: A freelance graphic designer working from home might choose a Private Mailbox to separate personal and business mail. With a Private Mailbox, the designer can use a professional address for business correspondence, receive packages from different courier services, and have the option to forward their mail to another address if they move or travel frequently.
Similarly, small businesses often use Private Mailboxes to maintain a professional appearance. Instead of using a home address for mail and packages, businesses use a Private Mailbox to receive mail securely and maintain privacy.
PMB in Healthcare: Ensuring Standardized Coverage
In healthcare, Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMBs) play a critical role in providing essential healthcare services to individuals covered by medical schemes. These benefits ensure that all members, regardless of the medical plan they are on, have access to necessary treatments for life-threatening conditions, chronic diseases, and other vital health services.
Real-World Example: In a healthcare scenario, a patient with a chronic condition such as diabetes may be covered under their medical scheme’s Prescribed Minimum Benefits. These benefits guarantee that the patient will receive essential care, including medications, regular check-ups, and necessary treatments. Without PMBs, the patient might not receive the care they need due to the limitations of certain medical plans, which could result in severe health complications.
The Prescribed Minimum Benefits (PMBs) not only ensure better healthcare access but also help reduce financial burdens, making healthcare more accessible for all, particularly in low-income communities or for those who need ongoing treatment.
Conclusion
To sum up, PMB meaning encompasses essential concepts like Performance Measurement Baseline in project management, ensuring efficient tracking, Prescribed Minimum Benefits in healthcare, and the benefits of a Private Mailbox (PMB) for secure, professional mail handling.
Understanding PMB in these areas helps you make informed choices, whether managing projects, securing your privacy, or accessing healthcare. By utilizing PMBs, you can enhance efficiency, security, and outcomes in both personal and professional settings.
FAQs
What is a PMB service?
A PMB service refers to a Private Mailbox service, where a private company provides individuals or businesses with a real street address for receiving mail and packages. Unlike a PO Box, PMBs allow mail to be accepted from all couriers (e.g., UPS, FedEx), and often include additional features such as mail forwarding and secure mail handling.
What does PMB mean in a mailing address?
In a mailing address, PMB typically refers to a Private Mailbox. It is a service that offers a real street address instead of just a PO Box number, allowing individuals and businesses to receive mail and packages from various delivery services. This can provide greater flexibility and privacy compared to a traditional PO Box.
What is a PMB used for?
A PMB (Private Mailbox) is used for receiving mail and packages at a real street address, providing more privacy and security than a PO Box. It is commonly used by businesses that want to maintain a professional image and by individuals who need a secure, flexible mailing address for receiving correspondence and parcels from various couriers.
What’s the difference between a PO box and a PMB?
The main difference between a PO Box and a Private Mailbox (PMB) lies in the type of address provided. A PO Box is a postal address at a post office that only accepts mail from USPS. In contrast, a PMB provides a real street address, which can receive mail and packages from all courier services, including UPS and FedEx. PMBs also often offer additional services like mail forwarding and 24/7 access, making them more versatile and secure.