NFT Art in 2025 | What It Is, Latest News & How to Create
Navigating the world of NFTs can be tough. The technical jargon and market complexities overwhelm many. Understanding how it works and its benefits can seem daunting.
This guide will clarify NFT art essentials, advantages, and steps for creation. You’ll gain the knowledge to confidently engage with digital art and explore its potential for artists and collectors.
What is an NFT Art?

NFT art, or non-fungible token art, represents digital artwork that is tokenized on a blockchain. Unlike traditional art, NFTs exist in digital form and are secured using blockchain technology.
This technology ensures that each piece of NFT is unique and cannot be replicated, providing a new level of ownership and authenticity in the digital art world.
NFT can take various forms, including digital paintings, animations, videos, and virtual reality experiences. The blockchain acts as a public ledger, recording all transactions and ownership transfers, thus ensuring the provenance of each piece of digital art.
The Latest NFT Art Trends in 2025
The world of NFT art continues to evolve rapidly in 2025, reshaping the meaning of digital investment and redefining how artists create, share, and sell their artworks. From digital paintings and drawings to high-value crypto collections, this year marks a shift in how collectors and rising artists engage with blockchain technology.
Breaking News and Market Insights
The latest news reveals that CryptoPunks, one of the most iconic NFT art collections, is still dominating the NFTs crypto market with $2.8 million in weekly sales. Despite earlier market dips, July saw a 47.6% rise in sales, hitting $574 million as collectors invested in digital images and rare creations with cultural significance.
In a surprising twist, Yuga Labs transferred ownership of the CryptoPunks artworks to the nonprofit Infinite Node Foundation, focusing on preserving these digital designs for exhibitions and history.
The Meaning of NFT Art in 2025
NFTs are unique blockchain-based creations that turn any picture, design, or image into a digital asset. This innovation has opened doors for artists to monetize their artworks while ensuring authenticity and ownership.
Creating and Promoting Your NFT Art
Learning how to create or how to make digital artworks has never been easier. Platforms now provide NFT creation services that guide artists through every step — from design to minting and promotion. If you’re a rising artist looking to stand out, focus on unique creations and learn how to promote your NFTart effectively across marketplaces and social platforms.
Explore different AI art styles to make your digital artwork stand out and attract collectors in the evolving NFT space.
Digital Investment and Future Potential
NFTs are no longer hype; they’re seen as serious digital investments. With the right artworks and promotion strategies, both established and rising artists can generate substantial income while contributing to the growth of blockchain-powered art markets.
Understanding concepts like the fair value gap can help artists and investors evaluate the true worth of their NFT artworks in the volatile digital market.
Differences Between NFT and Traditional Art
NFT Art
NFT uses digital tools like graphic design programs, 3D modeling software, and animation platforms. Artists can create various forms such as digital paintings, animations, videos, and virtual reality experiences.
The digital nature of NFTs allows for more experimentation and innovation, as artists can easily edit and manipulate their creations. The blockchain records transactions and ownership transfers, ensuring provenance and providing a transparent, immutable record.
Each NFT contains metadata with information about the artwork, the artist, and the ownership history, making it easy to verify authenticity. Digital art can be sold directly to collectors through online marketplaces such as OpenSea, SuperRare, and Foundation.
This direct-to-consumer model allows artists to reach a global audience without intermediaries. Additionally, smart contracts ensure artists earn royalties on secondary sales, providing ongoing revenue.
Traditional Art
Traditional art uses physical materials such as paint, canvas, and paper. Artists work with tangible media to create their masterpieces. Ownership and provenance in traditional art are often documented through certificates of authenticity, receipts, and physical records.
This can sometimes be lost or forged, leading to disputes over the authenticity of a piece. Traditional art is typically sold through galleries, auctions, and art dealers, relying on intermediaries to facilitate sales and promote the work.
In the traditional art market, artists only earn money from the initial sale of their work, with no compensation from subsequent resales, unlike NFT. This limitation means traditional artists miss out on potential ongoing revenue from the resale of their pieces.
The Evolution of NFT
The history of NFT art is relatively short but highly dynamic. Its origins can be traced back to the early 2010s when digital artists began exploring blockchain technology as a means to authenticate and sell their digital creations.
One of the first significant milestones was the launch of CryptoPunks in 2017, a collection of 10,000 unique 24×24 pixel art characters. This project, created by Larva Labs, gained widespread attention and set the stage for the explosion of NFTs.
History and Origins
The concept of NFTs started gaining traction with the advent of blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum, which introduced the ERC-721 standard for non-fungible tokens.
This standard enabled the creation and trading of unique digital assets on the blockchain. Early projects like CryptoPunks and CryptoKitties demonstrated the potential of NFTs and garnered significant interest from the tech and art communities.
Significant Milestones and Trends
Several milestones have marked the evolution of NFTs. In 2020, the NFT market saw a surge in activity, with artists and collectors flocking to platforms like OpenSea and SuperRare.
High-profile sales, such as Beeple’s “Everydays: The First 5000 Days,” which sold for $69 million at Christie’s auction house in 2021, brought mainstream attention to NFTs. This landmark sale highlighted the growing acceptance and value of digital art within the broader art market.
The rise of NFTs has also been characterized by various trends, including the emergence of virtual galleries and exhibitions, where artists can showcase their work in immersive digital environments.
Additionally, collaborations between traditional and digital artists have become increasingly common, bridging the gap between the physical and digital art worlds. Market volatility and speculation can impact the value of NFTs, similar to how the probability of default (PD) affects financial investments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of NFT
Advantages of NFT
NFT art offers numerous benefits for artists and collectors. One significant advantage for artists is the ability to prove ownership and authenticity using blockchain technology. This transparency ensures that each piece of art is original and traceable, reducing the risk of forgery and fraud.
Additionally, artists can reach a global audience by selling their work on online marketplaces such as OpenSea, SuperRare, and Foundation. This direct-to-consumer model eliminates the need for intermediaries and allows artists to retain a larger share of the profits.
Exploring NFTs beyond unleashing their full potential can open up new creative and financial opportunities for artists and collectors. Another advantage is the potential for ongoing revenue through royalties. Smart contracts can be programmed into NFTs to ensure that artists receive a percentage of each resale.
This feature incentivizes artists to create high-quality work and provides them with a continuous income stream. Collectors also benefit from the unique ownership and investment opportunities offered by NFTs.
The ability to verify provenance and authenticity on the blockchain adds value and trust to each piece of art. Additionally, collectors can easily transfer and resell NFTs, providing liquidity and flexibility in the art market.
Disadvantages of NFT
Despite its advantages, NFT also has several drawbacks. One major concern is the environmental impact of blockchain technology. The energy consumption required to mint and trade NFTs is significant, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental degradation. This has raised ethical questions about the sustainability of NFT.
Another disadvantage is the potential for market volatility and speculation. The value of NFTs can be highly unpredictable, with prices fluctuating rapidly based on market trends and demand. This can make it challenging for both artists and collectors to assess the long-term value of their investments.
Additionally, the NFT market is still relatively new and unregulated, which can lead to issues such as fraud, copyright infringement, and a lack of consumer protection. Artists and collectors must exercise caution and conduct thorough research before engaging in the NFT market.
Collectors must also consider potential tax implications, such as capital gains tax, when selling NFT art.
Cryptocurrency and NFT Art

Cryptocurrencies play a crucial role in the NFT ecosystem, enabling seamless transactions, investments, and trading. The most commonly used cryptocurrency in the NFT space is Ethereum (ETH), thanks to its robust blockchain and smart contract capabilities.
As cryptocurrencies become more mainstream and widely accepted, the NFT market is expected to see increased participation and investment. This integration facilitates the purchase, trading, and minting of NFTs, opening up new possibilities for digital ownership and creativity.
Understanding different currencies, such as the Saudi Arabian currency (SAR), and customer-to-customer (C2C) transactions, is important for navigating the NFT market.
Blockchain and NFTs
Blockchain technology is the backbone of NFTs. It provides a decentralized and secure way to verify ownership and provenance. Each NFT is minted on a blockchain, creating a permanent record of its existence and ownership history.
This transparency ensures that each piece of digital art is unique and cannot be replicated or forged. Ethereum’s blockchain is particularly popular due to its support for smart contracts, which automate and enforce the terms of NFT transactions.
Trading NFTs
The trading of NFTs is facilitated by online marketplaces that accept cryptocurrency payments. Platforms like OpenSea, SuperRare, and Foundation allow users to buy, sell, and auction NFTs using cryptocurrencies.
These platforms provide a seamless and user-friendly experience, making it easy for artists and collectors to engage in the NFT market. Additionally, the use of smart contracts ensures that artists receive royalties from secondary sales, providing ongoing revenue.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency Integration
- Seamless Transactions: Cryptocurrencies enable quick and secure transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts automate complex transactions, ensuring that terms are met and royalties are paid.
- Global Reach: Cryptocurrencies are borderless, allowing artists and collectors from around the world to participate in the NFT market.
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology provides robust security features, protecting the integrity of NFT transactions.
|
Aspect |
Description |
|
Primary Cryptocurrency |
Ethereum (ETH) is the most commonly used cryptocurrency in the NFT space. |
|
Transactions |
Cryptocurrencies enable seamless purchasing, trading, and minting of NFTs. |
|
Smart Contracts |
Smart contracts ensure royalties and facilitate complex transactions. |
|
Global Reach |
Cryptocurrencies allow worldwide participation in the NFT market. |
|
Enhanced Security |
Blockchain technology provides robust security for NFT transactions. |
|
Increased Participation and Investment |
Mainstream acceptance of cryptocurrencies drives NFT market growth. |
|
Digital Ownership and Creativity |
Integration of crypto and NFTs enhances digital ownership possibilities. |
Creating NFT
Tools and Software Required
To create NFT art, you’ll need various digital tools and software. Popular programs include Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and Procreate for digital painting and graphic design. For 3D modeling, artists use software generators like Blender, ZBrush, and Maya.
Animation tools like After Effects and Cinema 4D are essential for creating animated NFTs. Additionally, you’ll need access to a cryptocurrency wallet and a platform to mint your NFTs, such as MetaMask and Mintable. NFTs finance aspects are crucial for artists and collectors looking to maximize their investments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Digital Art
- Conceptualize Your Art: Start by brainstorming and sketching your ideas. Consider the theme, style, and message you want to convey.
- Create Your Digital Art: Use graphic design software, websites, or 3D modeling tools to create your artwork. Experiment with different techniques and styles to bring your vision to life.
- Prepare Your Files: Ensure your digital files or gallery are in the correct format and resolution. Common formats include PNG, JPEG, and GIF for static pictures, and MP4 for animations.
Minting Your NFT Art
Minting is the process of converting your digital art into an NFT on the blockchain. Here’s how to mint your NFT:
- Set Up a Cryptocurrency Wallet: Download a wallet like MetaMask and create an account. Secure your wallet with a strong password and back up your recovery phrase.
- Choose a Minting Platform: Select a platform like Mintable, Rarible, or OpenSea to mint your NFT. Each platform has its features and fees, so choose one that suits your needs.
- Upload Your Art: Follow the platform’s instructions to upload your digital art file. Add a title, description, and any relevant metadata to your NFT.
- Set Your Price: Decide whether you want to sell your NFT at a fixed price or through an auction. Consider the value of your art and the current market trends.
- Mint and List Your NFT: Complete the minting process by paying the associated gas fees. Once minted, your NFT will be listed on the chosen platform for sale.
Selling NFT
How to List and Sell NFT
Listing and selling NFTs is a straightforward process but requires attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a Marketplace: Select a platform like OpenSea, SuperRare, or Foundation where you want to list your NFT. Each platform has unique features and fee structures, so choose one that fits your needs.
- Upload Your NFT: Follow the platform’s instructions to upload your NFT. Provide a clear and engaging title, description, and relevant tags to make your NFT attractive to potential buyers.
- Set Pricing Options: Decide whether to sell your NFT at a fixed price or through an auction. Fixed-price listings offer immediate sales, while auctions can drive higher bids but require more patience.
- Promote Your NFT: Use social media and other online channels to promote your NFT. Engage with potential buyers, art communities, and influencers to increase visibility and interest in your work.
Strategies and Tips for Successful Sales
- Build a Strong Portfolio: Showcase a cohesive and high-quality collection of your work. Consistency in style and theme can attract serious collectors.
- Engage with the Community: Be active on social media platforms, NFT forums, and art communities. Building relationships with fellow artists and collectors can increase your chances of making sales.
- Leverage Collaborations: Partner with other artists or influencers to create collaborative works. This can expand your reach and introduce your art to new audiences.
- Offer Exclusivity: Limited editions or unique perks, such as access to future artworks or behind-the-scenes content, can make your NFT more desirable.
- Monitor Market Trends: Stay updated on the latest trends and market dynamics in the NFT space. Understanding buyer preferences and pricing strategies can help you optimize your listings.
Major NFT Marketplaces and Platforms

Several platforms have gained prominence in the NFT art world:
- OpenSea: The largest NFT marketplace, supporting a wide range of digital assets and offering user-friendly tools for buying and selling.
- SuperRare: A curated marketplace for high-quality digital art, emphasizing artist verification and exclusivity.
- Foundation: A platform focused on creative expression and community building, where artists can mint and auction their NFTs.
- Rarible: A decentralized marketplace allowing artists to mint, buy, and sell NFTs, with a strong focus on community governance.
- Mintable: Offers tools for minting and selling NFTs, catering to both beginners and experienced artists.
The Market for NFT
The NFT art market has experienced tremendous growth and transformation in recent years. This expansion is driven by increasing interest from artists, collectors, and investors alike.
Understanding the current market trends, popular artists, and future growth potential can help you navigate this dynamic space. NFT platforms operate similarly to business-to-consumer (B2C) commerce, where artists sell directly to consumers.
Current Market Trends and Statistics
The NFT market has seen exponential growth, with sales reaching billions of dollars. High-profile sales, like Beeple’s “Everydays: The First 5000 Days,” have brought significant attention to NFTs.
Platforms like OpenSea and SuperRare have facilitated millions of transactions, making NFTs more accessible to a global audience. Additionally, the emergence of virtual galleries and exhibitions has provided new opportunities for artists to showcase their work.
Popular NFT Artists and High-Value Sales
Several artists have gained prominence in the NFT art world. Beeple, whose real name is Mike Winkelmann, is one of the most well-known figures, with his artworks fetching millions of dollars.
Other notable artists include Pak, Fewocious, and XCOPY, all of whom have made substantial contributions to the NFT scene. High-value sales of their artworks have further validated the potential and value of digital art.
Market Opportunities and Future Growth Potential
The future of the NFT market looks promising, with numerous opportunities for artists and collectors. As more mainstream artists and celebrities enter the space, the market is expected to continue its expansion.
The integration of NFTs with other technologies, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, will likely create new and immersive art experiences. Additionally, the development of more sustainable blockchain solutions could address environmental concerns and enhance the appeal of NFTs.
As the market evolves, staying informed about trends and developments will be crucial for success. Engaging with the NFT community, participating in virtual events, and continually exploring new platforms can help you stay ahead in this rapidly changing landscape.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
As the popularity of NFTs grows, it is essential to address the ethical and environmental concerns associated with them. Understanding these considerations can help artists and collectors make informed decisions.
Environmental Impact
One of the primary concerns surrounding NFTs is their environmental impact. The process of minting and trading NFTs requires significant energy consumption due to the underlying blockchain technology.
Most NFTs are currently minted on the Ethereum blockchain, which uses a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism. This mechanism involves complex computations that consume a substantial amount of electricity, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental degradation.
To mitigate this impact, some artists and platforms are exploring more sustainable alternatives. For example, Ethereum plans to transition to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is expected to reduce energy consumption significantly. Additionally, other blockchain networks, such as Tezos and Flow, are gaining popularity for their eco-friendly approaches to minting NFTs.
Addressing Plagiarism and Fraud
The digital nature of NFTs can lead to issues of plagiarism and fraud. Unscrupulous individuals may attempt to mint and sell copies of original artworks without the artist’s permission. This can undermine the value and authenticity of genuine NFTs.
To combat this, artists and platforms are implementing measures to verify the authenticity and ownership of NFTs. Verification processes, such as artist verification badges and blockchain-based certificates of authenticity, help ensure that the art being sold is legitimate. Additionally, artists can use watermarks and other digital signatures to protect their work from unauthorized duplication.
Ethical Practices for Artists and Collectors
Both artists and collectors have a role to play in maintaining ethical practices within the NFT space. Artists should be transparent about their work, providing accurate information about the creation process, materials used, and any collaborative efforts. They should also respect the intellectual property rights of others and avoid creating or selling art that infringes on existing copyrights.
Collectors, on the other hand, should conduct thorough research before purchasing NFTs. Verifying the authenticity and provenance of the artwork, understanding the artist’s reputation, and being aware of market trends can help collectors make informed decisions. Additionally, collectors can support environmentally conscious artists and platforms that prioritize sustainability.
The Future of NFT Art
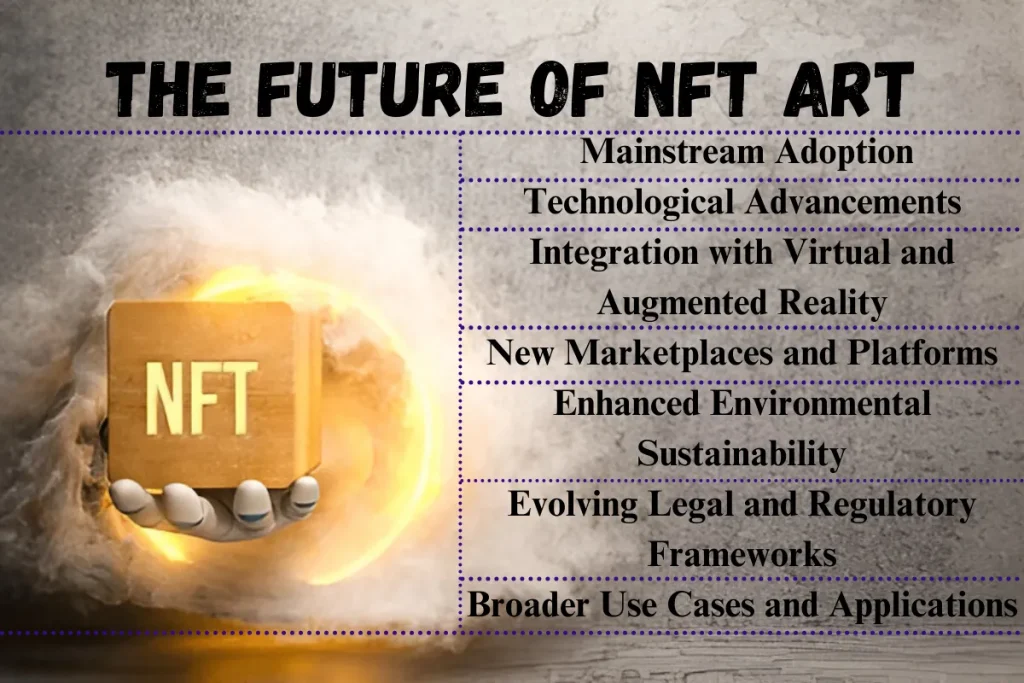
The future of NFT holds significant promise as technology and market dynamics continue to evolve. Several key trends and developments are expected to shape the future landscape of NFT:
1. Mainstream Adoption
As more mainstream artists, celebrities, and brands enter the NFT space, the market is likely to expand further. This increased visibility and acceptance can attract a broader audience, including those who may have been hesitant to engage with NFTs initially. Mainstream adoption can lead to greater legitimacy and recognition of NFTs as a valid form of artistic expression and investment.
2. Technological Advancements
Advancements in blockchain technology and other related fields will continue to enhance the capabilities and features of NFTs. The transition of Ethereum to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, known as Ethereum 2.0, is expected to reduce energy consumption and improve scalability.
Additionally, the development of layer-2 scaling solutions and interoperability between different blockchains can make NFT transactions faster and more cost-effective.
3. Integration with Virtual and Augmented Reality
The integration of NFTs with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is set to create immersive and interactive art experiences. Artists can develop virtual galleries, exhibitions, and installations where viewers can engage with NFTs in entirely new ways. This convergence of technologies can revolutionize how art is created, displayed, and experienced.
4. New Marketplaces and Platforms
The emergence of new NFT marketplaces and platforms will provide artists with more opportunities to showcase and sell their work. These platforms may offer unique features, such as enhanced curation, artist support, and community engagement. As competition among marketplaces increases, artists can benefit from better terms, lower fees, and more exposure.
5. Enhanced Environmental Sustainability
Addressing environmental concerns will be a priority for the future of NFTs. As blockchain networks transition to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and sustainable practices, the environmental impact of minting and trading NFTs is expected to decrease. This shift can attract environmentally conscious artists and collectors who prioritize sustainability.
6. Evolving Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
As the NFT market matures, legal and regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve to address issues such as copyright protection, scam prevention, and consumer rights. Clear guidelines and regulations can provide greater security and trust for artists and collectors, fostering a more stable and transparent market.
7. Broader Use Cases and Applications
Beyond traditional art, NFTs are expected to find applications in various industries, including gaming, music, fashion, and entertainment. The versatility of NFTs can enable new forms of digital ownership, experiences, and monetization. This diversification can drive innovation and create new opportunities for artists and creators across different fields.
Conclusion
The journey through the world of NFT art is vibrant and ever-changing. It combines digital creativity with blockchain technology. Understanding the differences between digital and traditional art, the process of creating and selling NFTs, and ethical considerations helps artists and collectors navigate this space. The future looks promising with technology advancements and wider adoption creating new opportunities.
Cryptocurrency plays a key role in the NFT ecosystem, enabling transactions and investments. Ethereum is the most commonly used cryptocurrency for NFTs, due to its blockchain and smart contracts. This integration allows for the purchase, trading, and minting of NFTs. It enhances digital ownership and creativity, making the market more accessible and exciting.
FAQs
What does NFT mean?
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token. It represents ownership or authenticity of a unique item or piece of content, such as digital art, on a blockchain.
Is NFT art worth anything?
Yes, NFT can be worth significant amounts. The value depends on the artist's reputation, the piece's uniqueness, and market demand. Some NFTs have sold for millions.
Why are artists against NFT?
Some artists oppose NFTs due to environmental concerns linked to blockchain's energy use. Others worry about plagiarism and market volatility affecting long-term value.
What Are The Costs Associated With Creating NFT Art?
Costs include minting fees on the blockchain, which vary by platform. Artists also invest in digital tools, software, and a cryptocurrency wallet for transactions.
What can you do with an NFT?
You can prove ownership, trade, sell, and auction NFTs. They can also provide access to exclusive content, virtual experiences, and integration into games and applications.






