What is a Hyperscaler? Explore Hyperscale Data Centers & Cloud Computing
Introduction to Hyperscalers
What is a Hyperscaler?

A hyperscaler is a company or entity that operates extremely large-scale data centers designed to handle massive amounts of computing resources, storage, and networking. These companies deliver cloud computing services on an enormous scale, enabling businesses to store, process, and manage data in real-time without having to build their infrastructure. The hyperscaler model offers unparalleled scalability, efficiency, and reliability, making it a preferred choice for businesses that need on-demand computing resources.
Hyperscalers are the backbone of modern cloud computing, providing services such as infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). Some of the most well-known hyperscalers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud.
What is Hyperscale Computing?
Hyperscale computing refers to a system of scaling IT resources, such as computing power and storage, to meet the demands of large applications or organizations. It is a highly efficient and flexible approach that allows for the quick addition of resources as needed, without disruption to service. The key characteristic of hyperscale computing is its ability to handle an exponentially increasing amount of data and workload, thanks to the architecture of the hyperscale data centers that power it.
These hyperscale data centers are typically composed of thousands or even millions of servers, which work together to provide massive computational power, redundancy, and data storage. Hyperscalers leverage these data centers to offer global reach and ensure that data is always available, regardless of the user’s location.
Hyperscalers vs Cloud Providers
While the terms cloud provider and hyperscaler are often used interchangeably, there are significant differences between the two. A cloud provider can refer to any company offering cloud computing services, from small-scale businesses to large enterprises. On the other hand, a hyperscaler is a subset of cloud providers, typically characterized by their massive infrastructure and capacity to serve millions of customers simultaneously.
Hyperscalers operate at a much larger scale compared to traditional cloud providers. They are built to handle extremely high levels of demand, offering both hyperscale cloud and data center hyperscaler services. The infrastructure of a hyperscaler is specifically designed for rapid expansion, allowing it to support the growing needs of businesses across different industries.
Hyperscalers provide essential hyperscale computing solutions to industries like e-commerce, social media, gaming, and healthcare, where data processing and storage needs are vast and ever-growing.
The Evolution of Hyperscalers in the Cloud Industry

From Data Centers to Cloud Marketplaces
The transition from traditional data centers to hyperscale data centers has been one of the most significant shifts in the cloud computing industry. In the past, businesses had to build and maintain their own physical data centers to store and process information. However, with the rise of hyperscalers, companies can now rent computing power, storage, and network resources from hyperscaler providers. This move toward shared infrastructure has allowed businesses to scale more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Hyperscalers have revolutionized how companies approach IT infrastructure. Instead of investing in physical hardware, businesses can now rely on cloud services that are not only scalable but also managed and maintained by the hyperscalers themselves. This change has given rise to the concept of hyperscale cloud services, where customers only pay for what they use, making it easier to adjust resources as needed.
As hyperscalers evolved, the traditional data center model gave way to more flexible and agile hyperscale data center solutions, leading to the growth of cloud marketplaces where businesses can access a wide range of services. These cloud hyperscalers are constantly innovating, enabling organizations to operate with greater flexibility, reliability, and scalability.
Hyperscalers and the 2000s Tech Boom
The early 2000s witnessed a technological revolution that laid the groundwork for the hyperscaler model we see today. With the growth of the internet and the increasing reliance on digital services, companies began to face challenges in managing the ever-increasing volume of data and the demand for high-performance computing. The solution came in the form of hyperscalers, whose massive infrastructure was designed to meet these new demands.
The success of companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), which emerged in the mid-2000s, signaled the dawn of the hyperscaler era. AWS, followed by other tech giants like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud, helped define what hyperscale computing could achieve. These companies invested heavily in hyperscale infrastructure, building large data centers across the globe, offering cloud services at scale.
The tech boom of the 2000s also saw the rise of new technologies that enabled hyperscalers to expand their services. Advancements in hyperscale connectivity, server virtualization, and automated data management allowed these companies to provide on-demand services to businesses at a fraction of the cost and time previously required for building physical infrastructure.
Innovation and Scalability: The Core of Hyperscalers
At the heart of hyperscalers’ success is their ability to innovate and scale quickly. These companies are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible with cloud computing, hyperscale data centers, and edge computing. The hyperscale cloud model allows businesses to scale their IT infrastructure quickly and easily, providing access to computing power whenever it is needed.
Hyperscalers are also leaders in hyperscale solutions like hyperscale storage, hyperscale servers, and hyperscale networking. These solutions are designed to handle vast amounts of data and process information at lightning speed. For example, AWS and Google Cloud utilize custom-built hyperscale data center architecture to ensure maximum efficiency, performance, and redundancy.
The scalability offered by hyperscalers allows businesses to start small and grow as needed, without the burden of managing their hardware. This flexible, pay-as-you-go model is what makes hyperscalers so attractive to both startups and large enterprises alike. By leveraging the power of hyperscalers, companies can access the computing resources they need without the upfront costs of traditional infrastructure.
How Hyperscalers Operate

What is a Hyperscale Data Center?
A hyperscale data center is a facility that houses vast quantities of IT resources, such as servers, storage devices, and networking equipment, all designed to operate at a large scale. Unlike traditional data centers that may host a few hundred to a few thousand servers, hyperscale data centers can support tens of thousands of servers working in tandem, providing massive computational power and storage capacity.
These data centers are built with redundancy and fault tolerance in mind, ensuring that operations remain unaffected even in the event of hardware failure or connectivity issues. Hyperscalers invest heavily in hyperscale infrastructure to support such large-scale operations. The architecture of these data centers is designed for flexibility, enabling rapid scaling as demand grows. They often use advanced technologies such as server virtualization, automated management, and energy-efficient cooling systems to enhance performance and minimize costs.
The hyperscale data center solutions provided by companies like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer businesses the ability to store and process data at an unprecedented scale. These centers are located in strategic regions across the globe, enabling hyperscalers to offer low-latency access and ensure high availability for their clients.
Hyperscalers support B2C commerce by providing the infrastructure that powers online marketplaces. With the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing, businesses can efficiently handle large volumes of transactions and customer data.
Hyperscale Cloud Providers and Their Services
The hyperscale cloud providers are the key players in the global cloud market, offering a range of cloud services that can scale to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. These services typically fall into three categories: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): This allows businesses to rent computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networks without owning the hardware. AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) and Google Compute Engine are prominent examples of IaaS offerings by hyperscalers.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): Hyperscalers offer PaaS solutions that provide platforms for developing, running, and managing applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure. Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine are major examples of this service.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS allows businesses to use applications over the internet without worrying about maintaining them. Common examples include Google Workspace and AWS WorkSpaces.
These hyperscale cloud providers enable businesses to scale their operations up or down based on demand, reducing the need for expensive on-premises infrastructure. By leveraging the power of hyperscalers, companies can access a vast array of services, ranging from cloud storage to advanced machine learning models, all within a secure and reliable environment.
How Do Hyperscalers Work?
Hyperscalers operate by providing vast pools of computing resources that businesses can tap into as needed. The core principle behind how hyperscalers work is elasticity—the ability to scale up or down based on demand, ensuring that businesses only pay for the resources they use.
The infrastructure that powers hyperscalers is distributed across multiple hyperscale data centers worldwide. These data centers are connected by a high-performance global network, ensuring that users can access services from any location with minimal latency. The services offered by hyperscalers are highly automated, with sophisticated hyperscale software and cloud management tools that allow businesses to monitor and control their resources in real-time.
One of the most important aspects of hyperscalers’ operations is the integration of edge cloud services and cloud hyperscalers. By extending their services to the edge of the network, hyperscalers are able to provide faster response times and improve the performance of applications that require real-time data processing, such as IoT devices and gaming platforms.
Hyperscalers also rely heavily on custom-built hyperscale servers and hardware to optimize performance. For instance, companies like Amazon and Google design their servers to handle specific workloads, ensuring that their systems are optimized for the high demands of hyperscale data centers.
Hyperscale Cloud: Benefits and Costs
The hyperscale cloud offers several key benefits to businesses:
- Scalability: One of the main advantages of hyperscalers is the ability to scale resources up or down depending on demand. Whether a business needs additional storage, computing power, or network bandwidth, hyperscale solutions allow it to do so without any disruption to operations.
- Cost-Efficiency: Hyperscalers operate on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning businesses only pay for the resources they use. This makes it much more affordable than maintaining an on-premises data center, where businesses would need to invest heavily in hardware and infrastructure upfront.
- Reliability: Hyperscalers offer high levels of reliability and uptime. With geographically distributed hyperscale data centers, businesses can be assured that their data is safe and accessible, even in the event of a local outage.
- Innovation: Hyperscalers are at the forefront of cloud computing innovation, constantly releasing new services and features. They also lead in areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics, which can help businesses unlock new capabilities and gain a competitive edge.
However, there are also costs associated with hyperscale cloud services. As businesses scale up their usage, the costs can increase, particularly if the cloud provider charges based on storage, data transfer, and computational power. Therefore, businesses need to carefully manage their cloud services and consider cost optimization strategies to avoid unexpected bills.
Hyperscalers facilitate seamless API integration, enabling businesses to connect various systems and applications within their cloud environments. This integration helps streamline operations and provides scalability, similar to how companies use cloud services to improve flexibility.
Key Players in the Hyperscaler Market
Who Are the Top Hyperscalers?

The hyperscaler market is dominated by a few key players, each offering a range of cloud computing services that cater to businesses of all sizes. These hyperscalers operate massive data centers around the world, providing everything from storage solutions to advanced machine learning platforms. Some of the top hyperscalers include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): As one of the largest and most well-known hyperscalers, AWS offers a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including compute power (EC2), storage (S3), and networking. AWS is widely regarded as the leader in cloud computing and has built an ecosystem of products and services for businesses across all industries.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure is another major player in the hyperscale cloud market, offering a wide array of cloud services ranging from IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Microsoft Azure is popular among enterprises due to its integration with existing Microsoft products, such as Windows Server, SQL Server, and Office 365.
- Google Cloud: Known for its strong focus on big data, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, Google Cloud has emerged as a significant hyperscaler. Google Cloud offers services like Google Compute Engine and Google Cloud Storage, and is especially popular with businesses leveraging analytics and AI technologies.
- Alibaba Cloud: A leader in the Asia-Pacific region, Alibaba Cloud has expanded rapidly in recent years and now ranks among the top hyperscalers globally. Alibaba’s cloud offering includes services like Elastic Compute Service (ECS), Cloud Storage, and Data Transmission Services.
- IBM Cloud: While not as large as the others, IBM Cloud plays a significant role in the hyperscaler market, particularly for enterprises seeking hybrid cloud solutions. IBM Cloud combines traditional IT with hyperscale cloud resources, offering businesses the flexibility to run workloads both on-premises and in the cloud.
Top 10 Hyperscalers
The top hyperscalers in the market include both established companies and emerging players who are quickly gaining ground. The top 10 hyperscalers are:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Tencent Cloud
- Huawei Cloud
- DigitalOcean
- Rackspace Technology
These companies are shaping the future of cloud computing by driving innovation, expanding infrastructure, and offering a wide variety of services for businesses looking to scale their operations efficiently. Each of these hyperscalers has its strengths, whether it’s advanced AI, hybrid cloud solutions, or specialized services for different industries.
What Are Examples of Hyperscalers?
Several hyperscalers have set the standard for the industry, leading the way with innovative products, massive infrastructure, and global reach. Some notable examples include:
- AWS: The largest hyperscaler by market share, AWS serves millions of customers globally, from small startups to large enterprises.
- Google Cloud: With a strong focus on AI and machine learning, Google Cloud is a popular choice for companies that require advanced analytics and data processing capabilities.
- Alibaba Cloud: A significant player in Asia, Alibaba Cloud has built an extensive network of hyperscale data centers across China and beyond, providing services to global businesses.
These hyperscalers have set the benchmark for cloud services, providing everything from storage and computing power to cutting-edge AI and machine learning capabilities. Each of them brings unique strengths to the table, helping businesses leverage the power of hyperscale computing to drive innovation and growth.
Hyperscaler Technology and Infrastructure

Hyperscale Infrastructure
The backbone of any hyperscaler is its infrastructure. Hyperscalers are renowned for their ability to scale computing resources rapidly to meet the ever-growing demand of modern businesses. This is achieved through vast networks of hyperscale data centers that are strategically located around the globe. These data centers are built to house thousands, sometimes millions, of servers, connected through high-bandwidth, low-latency networks that ensure smooth communication and performance across regions.
Hyperscale infrastructure is designed with reliability, scalability, and flexibility in mind. These facilities are equipped with advanced technologies such as automation, virtualization, and energy-efficient cooling systems to maximize operational efficiency. For instance, hyperscalers like AWS and Google Cloud use proprietary hardware and custom-built hyperscale servers to deliver high-performance computing at a global scale. Their hyperscale data center solutions also include redundant power systems, cooling solutions, and backup systems to ensure uninterrupted service.
By utilizing hyperscale infrastructure, businesses gain access to powerful resources without the need to invest in their own physical data centers. This infrastructure enables companies to scale rapidly, adapt to changing needs, and access cloud services with low latency.
The fiber optic color code system is an essential part of hyperscale data centers, as it helps organize and identify high-speed connections that power large-scale cloud operations. Understanding proper cable management ensures efficient data transmission in hyperscale environments.
Hyperscale Data Center Solutions and Architecture
The architecture of a hyperscale data center is quite different from that of traditional data centers. Hyperscalers build their data centers with one goal in mind: scalability. These data centers are modular, meaning that new servers, storage units, and networking equipment can be added with minimal disruption to existing operations. The design ensures that as businesses grow and their data requirements increase, hyperscalers can expand their infrastructure seamlessly.
Key elements of hyperscale data center architecture include:
- Modular design: Allows for rapid expansion and scaling based on demand.
- High-density storage: Supports large-scale data storage solutions, enabling the handling of vast amounts of data.
- Virtualization: Optimizes hardware utilization, allowing hyperscalers to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server.
- Cloud-native design: The architecture is specifically built to support cloud computing needs, with flexibility and elasticity in mind.
For businesses, this architecture provides a competitive advantage, offering them access to cutting-edge cloud technologies that are capable of supporting demanding workloads like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics.
When building hyperscale data centers, choosing the right cables is crucial. The debate between Cat6 vs Cat5 cables comes down to the need for higher bandwidth and faster data transfer speeds, making Cat6 the preferred choice for modern hyperscale networks.
The Role of Hyperscale Connectivity
Hyperscale connectivity is a critical component of the infrastructure that enables hyperscalers to deliver fast, reliable, and low-latency cloud services. These companies operate vast networks of fiber-optic cables and high-speed interconnects between data centers. This allows them to transfer data between regions quickly and efficiently, providing a seamless experience for end users.
Hyperscalers also use edge cloud services to bring computing resources closer to the end user. By placing computing power at the “edge” of the network, hyperscalers reduce latency and improve performance for applications that require real-time data processing, such as IoT (Internet of Things) and gaming.
With the increasing need for hyperscale cloud services in industries like e-commerce, healthcare, and financial services, hyperscalers invest heavily in hyperscale connectivity to ensure the uninterrupted flow of data. By leveraging global networks of data centers and edge locations, they can deliver services that are highly available and responsive, even in remote regions.
The Role of Hyperscale Software and Automation
Hyperscalers rely heavily on custom-built hyperscale software and automation to manage their vast infrastructure. These systems help monitor and control data center operations, from load balancing and resource allocation to security and disaster recovery.
Automation plays a key role in the efficiency of hyperscalers, allowing them to automatically scale resources up or down based on demand. For example, when demand for computing resources increases, the software can automatically allocate additional servers and storage, ensuring optimal performance. Similarly, when demand decreases, the system can scale down to avoid wasted resources, thus optimizing costs for both the hyperscaler and its customers.
By leveraging hyperscale software and automation, hyperscalers can maintain the reliability and efficiency of their services while minimizing the need for manual intervention. This not only helps hyperscalers deliver fast and responsive services but also allows businesses to benefit from lower operational costs and increased agility.
Hyperscalers and the Future of Cloud Computing
Emerging Trends in Hyperscale Cloud Computing
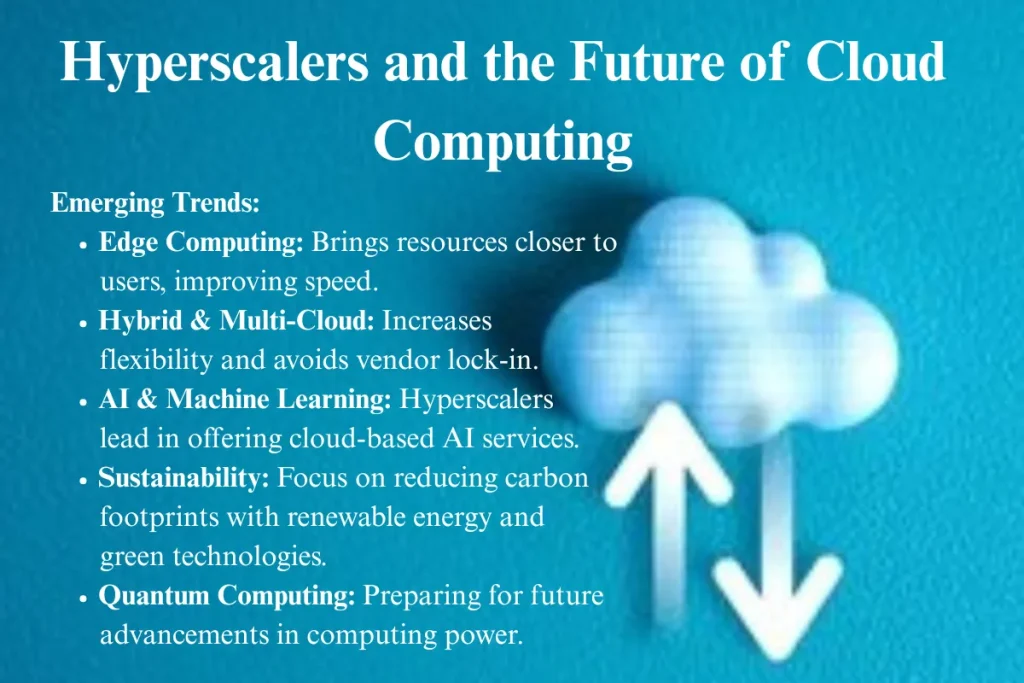
The landscape of hyperscale cloud computing is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Some of the key trends shaping the future of hyperscalers include:
- Edge Computing and Distributed Infrastructure: As the demand for real-time processing and low-latency services grows, hyperscalers are increasingly investing in edge cloud services. Edge computing places computational resources closer to end users, reducing the distance data must travel, improving speed, and enhancing application performance. This trend is particularly important for industries like IoT (Internet of Things), autonomous vehicles, and real-time data analytics.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Many businesses are adopting hybrid cloud and multi-cloud strategies to avoid vendor lock-in, increase flexibility, and optimize performance. Hyperscalers are evolving to offer solutions that can seamlessly integrate with on-premises infrastructure, other cloud providers, and edge environments, enabling companies to create a cloud infrastructure that fits their specific needs.
- AI and Machine Learning: Hyperscalers are at the forefront of AI and machine learning development, offering cloud-based AI tools and machine learning platforms to help businesses innovate. This includes services like predictive analytics, natural language processing, and computer vision, which enable organizations to gain insights from large datasets and drive automation.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: With growing concerns about climate change, hyperscalers are placing more emphasis on sustainability. Many hyperscalers are working to make their data centers energy-efficient and powered by renewable energy sources. Additionally, innovations like liquid cooling and green data centers are helping hyperscalers reduce their carbon footprint and become more environmentally friendly.
- Quantum Computing: Though still in its early stages, quantum computing is expected to revolutionize computing power in the future. Hyperscalers are investing in quantum computing research and infrastructure, preparing for its eventual integration into their cloud offerings. Quantum computing could dramatically enhance the performance of certain tasks, particularly in fields like cryptography, drug discovery, and material science.
These emerging trends show how hyperscalers are not only adapting to current demands but are also positioning themselves to drive future innovations in cloud computing.
Hyperscale Data Center Market
The hyperscale data center market is experiencing rapid growth. As more businesses move to the cloud, the demand for hyperscale data centers is increasing globally. These large-scale facilities are becoming more sophisticated, offering greater efficiency, scalability, and performance.
Hyperscale data centers are not only growing in size but also becoming more specialized. For instance, some hyperscalers are focusing on cloud hyperscale data centers that cater specifically to AI and machine learning workloads. Others are enhancing their data center infrastructure to support high-performance computing (HPC) for industries like finance and healthcare.
The hyperscale computing market is expected to continue its upward trajectory as more companies embrace cloud-first strategies. This growth is supported by increased investments in both hardware and software innovations, as well as the adoption of 5G networks and IoT devices that require large-scale data processing and storage.
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud-based applications for multimedia, understanding screen resolution capabilities becomes important. Hyperscalers enable the use of high-resolution content, such as 4K streaming or interactive displays, by offering the computing power required to support such high-demand use cases.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Hyperscalers
As concerns about environmental sustainability grow, hyperscalers are making significant strides to reduce their carbon footprint. Hyperscalers like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have committed to powering their data centers with renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
Sustainability in hyperscale cloud computing is a major focus. These companies are investing in technologies such as liquid cooling and advanced energy-efficient hardware to reduce power consumption. Additionally, hyperscalers are working with their customers to help them build greener cloud infrastructures by providing tools for carbon tracking and offering sustainable cloud solutions.
Many hyperscalers are also looking into the long-term environmental impact of their operations. For example, Google Cloud has been carbon neutral since 2007, and Microsoft has committed to becoming carbon negative by 2030. These efforts are setting a new standard in the industry, proving that hyperscale cloud services can be both efficient and sustainable.
Future Trends in Hyperscale Cloud
The hyperscale computing landscape is evolving rapidly, and several trends are likely to shape the future of hyperscalers:
- Increased Demand for Custom Hardware: As workloads become more specialized, hyperscalers are designing custom hyperscale servers to optimize for specific tasks like machine learning or high-performance computing.
- The Expansion of Edge and 5G: With the proliferation of edge computing and 5G networks, hyperscalers are expected to continue expanding their infrastructure to support applications that require low-latency data processing.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation: Hyperscalers will continue to integrate AI and automation into their cloud services to optimize resource management, enhance security, and provide more efficient services.
- Rise of Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud: Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies to avoid dependence on a single provider, and hyperscalers are adapting to offer hybrid cloud solutions that combine the benefits of public and private clouds.
As businesses store more sensitive data in hyperscale cloud environments, ensuring accurate data verification is critical for maintaining security and compliance. Hyperscalers play a key role in providing the infrastructure for secure and reliable data verification processes.
Challenges and Considerations for Hyperscalers

Vendor Lock-In and Dependency
One of the primary challenges for businesses utilizing hyperscalers is the risk of vendor lock-in. As companies become deeply integrated into a hyperscaler’s ecosystem, migrating away from that provider can become costly and complex. Hyperscalers often offer services that are highly optimized for their infrastructure, making it difficult to move workloads to another cloud provider without significant changes to the architecture or functionality.
Vendor lock-in occurs when businesses rely on proprietary technologies or platforms that cannot be easily replicated by other providers. While hyperscalers offer robust cloud services that meet a wide range of business needs, companies must carefully consider their long-term dependence on a single provider. This dependence can create challenges in terms of flexibility and negotiating better terms, especially as their data and applications grow.
To mitigate the risks of vendor lock-in, businesses should consider a multi-cloud strategy, where workloads are distributed across several cloud providers, reducing the dependency on a single hyperscaler. Additionally, adopting open-source solutions and building architectures that can work across different clouds can provide more flexibility in the future.
Staff augmentation is often necessary for businesses adopting hyperscaler services, as they may need additional expertise to manage and optimize their cloud infrastructure. With the rapid expansion of hyperscale cloud solutions, companies often require specialized skills to maximize the benefits of these services.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
As businesses move their data to the hyperscale cloud, concerns over data privacy and security become paramount. While hyperscalers invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with regulations, businesses still need to be proactive in ensuring their data remains secure.
Data privacy concerns are particularly important for industries that handle sensitive information, such as healthcare, finance, and government sectors. Many hyperscalers adhere to strict standards like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), but companies must ensure that their cloud provider meets the specific compliance requirements relevant to their industry.
The massive scale of hyperscalers means that they are prime targets for cyberattacks. Therefore, companies must not only rely on the security measures provided by the hyperscaler but also implement their security protocols, such as data encryption, monitoring, and regular audits, to protect their data from breaches.
Cost Optimization and Management
While hyperscale cloud services provide significant cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure, managing these costs can be challenging. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, businesses might struggle to keep track of how much they are spending on cloud resources, especially as they scale.
To optimize cloud costs, businesses should implement strategies like:
- Resource allocation: Only provision resources when needed, and scale down during off-peak hours.
- Automation: Use automated tools to turn off unused resources and manage costs more efficiently.
- Cost management tools: Many hyperscalers offer cloud cost management tools that allow businesses to track and manage their spending on cloud services.
Despite the potential for cost optimization, businesses must be vigilant to avoid overspending as their use of hyperscale services grows. Regular monitoring and adjusting usage based on demand will be key to keeping cloud costs under control.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
Another challenge that hyperscalers face is ensuring that their services meet the legal and regulatory requirements of different regions. With data sovereignty becoming a major concern, businesses must ensure that their data is stored and processed in compliance with the laws of the countries they operate in.
Hyperscalers typically operate global networks of data centers, but not all regions may have the same data protection laws. For instance, the European Union has strict data privacy laws (GDPR), while the United States has its own set of regulations (such as CCPA for California residents). Companies using hyperscalers must ensure that the provider’s data centers are compliant with the required standards and that their data is stored in the right geographic location.
To navigate these regulatory challenges, businesses should choose hyperscalers that offer transparent compliance policies and provide options for data residency. They should also work closely with legal teams to ensure that data usage aligns with regional laws.
Network Latency and Performance
As businesses rely more on cloud hyperscalers, one concern that often arises is network latency. Although hyperscalers have global data center infrastructures, the distance between the data center and the end user can introduce latency, especially for applications that require real-time processing, such as gaming, IoT, and streaming services.
Hyperscalers are continually working to improve the performance of their networks by building more edge data centers, bringing resources closer to end-users, and reducing latency. However, businesses must consider the location of their target audience and ensure that their hyperscaler’s data centers are positioned to provide the best performance.
To address network latency, businesses can deploy a combination of strategies, such as:
- Choosing a hyperscaler with a global network of edge data centers.
- Leveraging Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for faster content distribution.
- Optimizing application architecture to ensure low-latency processing.
Conclusion
Hyperscalers are fundamentally transforming the cloud computing landscape. They have introduced an unprecedented level of scalability, flexibility, and efficiency to businesses worldwide, enabling them to leverage massive amounts of computing power, storage, and networking without the need to maintain their infrastructure. By providing hyperscale cloud services, these companies have made it easier for organizations of all sizes to innovate, scale, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital world.
The role of hyperscalers in the evolution of cloud computing is indispensable. They have not only democratized access to cutting-edge technologies but also paved the way for innovations in fields like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. With their hyperscale data centers, global reach, and powerful computing resources, hyperscalers continue to drive the digital transformation of industries ranging from healthcare and finance to e-commerce and entertainment.
In addition to enabling businesses to scale quickly, hyperscalers also support hybrid cloud strategies and multi-cloud solutions, which provide businesses with greater flexibility and reduce the risks associated with relying on a single provider. As more companies shift their operations to the cloud, the demand for hyperscalers is expected to grow, making them even more integral to the future of the digital economy.
Key Takeaways
- Scalability and Flexibility: Hyperscalers offer businesses the ability to scale computing resources quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for companies experiencing rapid growth or fluctuating demand.
- Global Reach: With their vast networks of hyperscale data centers, hyperscalers provide low-latency services and high availability to customers around the world.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure, hyperscalers allow businesses to save on upfront capital costs and instead pay only for the resources they use.
- Innovation: Hyperscalers are driving technological innovation, especially in areas like AI, ML, and edge computing, helping businesses unlock new opportunities.
- Challenges and Considerations: While hyperscalers offer numerous benefits, businesses must carefully consider challenges such as vendor lock-in, data privacy, and network latency before fully adopting hyperscale services.
- Sustainability: As hyperscalers continue to expand their services, many are placing a strong emphasis on sustainability, investing in renewable energy and energy-efficient infrastructure to reduce their environmental impact.
Hyperscalers are not just shaping the present of cloud computing; they are defining the future of how businesses will store, process, and manage data. As more organizations move to the cloud, the influence of hyperscalers will only continue to grow. The ability to scale infrastructure quickly, innovate rapidly, and maintain high levels of service availability will continue to drive their success, making them the backbone of the digital world.