GPU Test & Benchmark | Compare Graphics Cards & Performance

The evolution of graphics processing units (GPUs) in modern computing has transformed the way we experience everything from gaming to professional applications like 3D rendering, video editing, and AI processing. Whether you’re a casual gamer, a content creator, or a computer enthusiast, the power of your GPU plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth performance, high-quality visuals, and overall system responsiveness.
In 2025, GPU technology has reached new heights, with the latest models offering cutting-edge performance and remarkable capabilities, such as ray tracing, AI-driven graphics, and support for high-resolution textures. However, with this growing demand for powerful GPUs, it has become essential to understand how well these components perform under different conditions. That’s where GPU testing and benchmarking come into play.
GPU testing, benchmarking, and optimization have become essential practices for anyone looking to get the most out of their graphics card. By running a series of tests and benchmarks, users can gauge the true performance of their GPU, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions about whether it’s time to upgrade or tweak their system. Whether you’re looking to compare the best graphics cards of 2025, evaluate GPU performance in gaming, or optimize your GPU for professional work, understanding how to test and benchmark your GPU is crucial.
What is GPU Testing? – Understanding the Basics
What is GPU Testing and Why is it Important?

GPU testing is the process of evaluating the performance of your graphics card under various loads and conditions. The primary objective of GPU testing is to assess how well the GPU handles real-world tasks, such as gaming, 3D rendering, or AI-powered tasks. It involves measuring performance metrics like frames per second (FPS), temperature, and power usage during testing scenarios, simulating gaming, rendering, or other intensive tasks.
Why is this important? As GPU technology becomes more advanced, it’s essential to ensure that your hardware can handle these increasing demands. Running GPU tests allows you to identify performance bottlenecks, check for hardware issues, and assess whether your current GPU setup can handle the latest games or software. Regular GPU testing ensures that your system performs optimally, keeping your hardware running smoothly and preventing performance degradation over time.
In 2025, as GPUs like the Nvidia RTX 3060, AMD Radeon RX 6800, and Nvidia Quadro cards push the boundaries of performance, GPU testing and benchmarking have become more important than ever. Whether you’re looking to test a GTX 1650, assess the performance of a 4070 Ti, or compare AMD and Nvidia graphics cards, testing is crucial to understand how your hardware stacks up against the competition and evolving software requirements.
If you’re new to understanding resolutions, check out how 4K Screen Resolution differs from 1080p and how your GPU can handle these variations.
Common GPU Testing Tools

When it comes to testing your GPU, several tools are available that provide in-depth insights into its performance. These GPU testing tools measure various aspects of the GPU, such as rendering quality, FPS, temperature, and stability. Some of the most widely used GPU benchmarking and stress testing tools include:
- 3DMark: One of the most popular GPU benchmarking tools, 3DMark is widely used to evaluate a GPU’s ability to render complex 3D scenes, measure FPS, and assess overall graphics performance. It provides comprehensive benchmark tests, including the Time Spy and Fire Strike tests, which are designed to push the GPU to its limits and assess its capabilities under stress.
- Heaven Benchmark: Developed by Unigine, Heaven Benchmark is another well-known tool that tests the GPU’s ability to handle complex 3D scenes and tessellation. It is widely used to stress-test GPUs and evaluate their ability to handle demanding graphical workloads. Users can also monitor real-time performance metrics such as FPS, temperature, and GPU load during the test.
- FurMark: If you’re looking to put your GPU under extreme stress, FurMark is the tool to use. It’s specifically designed for stress testing, making it ideal for identifying potential issues like overheating or stability problems. FurMark is often used to simulate the most demanding tasks and assess how the GPU responds under heavy loads.
- Passmark: Another powerful tool for GPU testing, Passmark allows users to benchmark not just their GPU, but also their CPU and memory performance. Passmark’s GPU test focuses on performance across different tasks, such as gaming, 3D rendering, and AI simulations. It provides an overall score that helps users evaluate GPU performance compared to others on the market.
- UserBenchmark: A free and accessible option for benchmarking, UserBenchmark tests a variety of system components, including the GPU, CPU, and storage. It allows users to compare their GPUs’ performance with others in the same price range, making it a great tool for budget-conscious gamers and professionals alike.
Each of these tools offers different features and testing scenarios, so choosing the right one depends on your needs. Whether you’re testing the Nvidia GTX 1650, comparing the RTX 3070, or benchmarking a Radeon RX 5700, it’s crucial to pick the right tool for the job.
Common GPU Metrics to Track
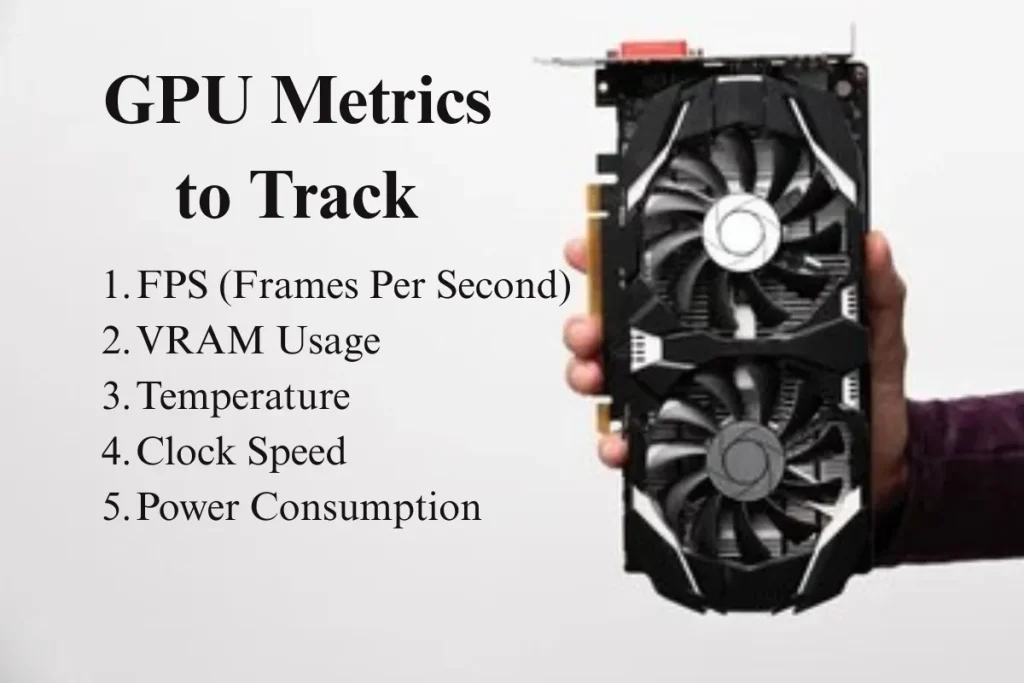
When you benchmark or stress-test your GPU, several key metrics help you evaluate its performance. Here are some of the most important GPU metrics to track during testing:
- FPS (Frames Per Second): FPS is a crucial metric for gaming and rendering. It measures how many frames your GPU can render per second, directly impacting the smoothness of the visuals. A higher FPS results in smoother gameplay and a better overall experience. Games like Cyberpunk 2077, Red Dead Redemption 2, and Assassin’s Creed Valhalla can be demanding on GPUs, so ensuring a high FPS in such games is essential.
- VRAM Usage: Video Random Access Memory (VRAM) is the memory used by the GPU to store textures, models, and frame buffers. VRAM usage is critical for high-resolution gaming and video editing. Checking VRAM usage during benchmarking will help you assess whether your GPU is being fully utilized or whether you need a graphics card with more VRAM (e.g., 8GB VRAM vs. 4GB VRAM).
Explore a detailed comparison of Cat5 vs Cat6 cables, as choosing the right network cable can also affect how your system interacts with the GPU, especially in multiplayer gaming.
- Temperature: The temperature of your GPU is another important metric to monitor during testing. GPUs can overheat during intensive workloads, which may lead to thermal throttling, where the GPU automatically reduces its performance to prevent damage. Tools like MSI Afterburner allow you to track GPU temperatures and ensure they stay within safe limits.
- Clock Speed: Clock speed refers to the rate at which the GPU processes instructions, and it plays a vital role in overall performance. During testing, you’ll want to keep an eye on clock speeds to ensure that your GPU is running at its maximum potential.
- Power Consumption: Power consumption is important, especially if you’re running a GPU-intensive workload for an extended period. A GTX 1650 may have a lower power consumption compared to an RTX 3080, and understanding your GPU’s power needs can help ensure your system’s power supply can handle the load.
How to Choose the Right GPU Benchmark Tool
Choosing the right GPU benchmarking tool depends on your testing goals. Are you testing for gaming performance? Or are you more focused on professional workloads, such as 3D rendering and video editing? Here are some tips to help you select the best GPU testing tool for your needs:
- For Gaming Benchmarks: If your primary concern is gaming performance, focus on tools that test FPS in real-world gaming scenarios. Tools like 3DMark and Heaven Benchmark provide in-depth performance analysis in demanding games, giving you an accurate representation of how your GPU will perform under different conditions.
- For Professional Workloads: For tasks like 3D rendering, video editing, and AI processing, you might want to consider tools that test GPU performance in professional applications. Tools like Passmark and UserBenchmark evaluate GPU performance across various workloads, ensuring your GPU can handle resource-heavy tasks.
- For Stress Testing: If you’re concerned about your GPU’s stability and thermals under extreme loads, FurMark is a great choice. It pushes the GPU to its limits, helping you identify issues like overheating or performance degradation during prolonged stress tests.
How to Benchmark Your GPU for Optimal Performance?
What is GPU Benchmarking?

GPU benchmarking is the process of testing the performance of your graphics processing unit (GPU) using specific tools and methods. The goal is to assess how well your GPU handles various tasks, such as gaming, video rendering, 3D modeling, and AI-driven computations. Through benchmarking, you can measure key performance indicators (KPIs) such as frame rates (FPS), GPU temperature, power consumption, and more.
In 2025, GPU benchmarking has evolved to include a variety of performance metrics, helping users understand how well their hardware performs in real-world applications. Whether you’re testing an entry-level GTX 1050 Ti or a high-end RTX 4070 Ti, benchmarking allows you to gain valuable insights into your GPU’s capabilities.
When benchmarking a GPU, you’re not just looking for raw performance numbers — you’re also seeking to optimize the system to ensure it functions well over time and in various environments. For gamers, this might mean achieving high FPS in titles like Cyberpunk 2077 or Battlefield V, while for professionals, it could mean maximizing render speeds in Blender or Autodesk Maya.
Interested in how these benchmark tests work? Learn about Performance Management techniques to optimize your system’s efficiency when running heavy benchmarks.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Benchmark Your GPU
Benchmarking your GPU requires a combination of the right tools, system setup, and methodology. Here’s a step-by-step guide to benchmarking your GPU for optimal performance.
1. Select the Right Benchmarking Tools
The first step in benchmarking your GPU is choosing the right tool for the job. Depending on the type of workload you’re testing — gaming, rendering, or AI processing — different tools might be more appropriate. Here’s a list of some of the most popular GPU benchmarking tools:
- 3DMark: One of the most comprehensive GPU benchmarking tools, 3DMark provides several tests that simulate demanding gaming and rendering scenarios. You can use it to measure FPS, GPU temperature, and overall performance in different settings.
- FurMark: This is a stress testing tool used to push your GPU to its limits. While it’s not ideal for gaming benchmarks, it’s excellent for testing GPU stability under extreme load.
- Heaven Benchmark: A tool specifically designed for measuring GPU performance in 3D rendering and gaming scenarios. It can give you valuable insights into your GPU’s ability to handle tasks like tessellation and complex graphical effects.
- UserBenchmark: This free tool is perfect for comparing your GPU’s performance with that of other users. It provides a quick, easy-to-understand summary of your GPU’s performance relative to others.
- Passmark: Great for measuring performance across a variety of workloads, Passmark offers benchmarks for both gaming and professional applications. It gives an overall performance score that you can compare against other GPUs.
2. Prepare Your System for Benchmarking
Before you start benchmarking, it’s important to make sure that your system is optimized for testing. This involves ensuring that your drivers are up to date, the system is running in a clean state, and any unnecessary background applications are closed.
- Update GPU Drivers: Ensure that your GPU drivers are up to date. Whether you’re using Nvidia or AMD, having the latest drivers installed ensures that your GPU operates at peak performance.
While installing your GPU, you might also encounter USB device not recognized issues. Here’s how to fix them and get your system ready for high-end gaming.
- Close Background Applications: Running unnecessary applications can reduce the overall performance of your GPU during benchmarking. Close applications that consume CPU, memory, and disk resources.
Before finalizing your choice, check out how a data validation vs verification approach ensures the accuracy of your system’s performance benchmarks.
- Ensure Proper Cooling: Overheating can cause your GPU to throttle its performance. Make sure that your system is well-ventilated and that your GPU’s cooling system (fans or liquid cooling) is functioning properly.
3. Run the Benchmarking Test
Now that your system is ready, it’s time to run the benchmark. Open your selected benchmarking tool and begin the test. Each tool will simulate a workload to assess how your GPU performs under stress.
- FPS Test: The most common test for gamers is the FPS benchmark, which measures how many frames your GPU can render per second. A higher FPS ensures smoother gameplay. Popular games like Red Dead Redemption 2 or Call of Duty are often used to test gaming performance.
- Stress Test: Tools like FurMark put a heavy load on your GPU to check its stability. This is crucial for identifying thermal throttling or power issues. Stress tests are particularly useful for long-duration testing or when pushing your GPU to its limits.
- Temperature Monitoring: During the benchmarking process, monitor your GPU’s temperature. Excessive heat can cause instability or permanent damage. Programs like MSI Afterburner and GPU-Z can provide real-time temperature readings while running benchmarks.
4. Analyze the Results
After running the test, you will be presented with a series of results that indicate how your GPU performed under the test conditions. These results typically include:
- FPS (Frames Per Second): A higher FPS means smoother performance. Most modern GPUs should aim for a minimum of 60 FPS for a smooth gaming experience, especially in fast-paced games.
- Temperature: Your GPU’s temperature should ideally remain below 85°C. Temperatures above this threshold may result in thermal throttling, which reduces the GPU’s performance to prevent overheating.
- Power Consumption: This metric shows how much power your GPU is consuming during the test. For example, the RTX 3070 Ti consumes around 290W, while a GTX 1650 might consume around 75W.
- VRAM Usage: VRAM (Video RAM) is crucial for rendering high-resolution textures and complex scenes. Ensure that your GPU has enough VRAM to handle the tasks you’re performing. For example, a GTX 1660 Super comes with 6GB of VRAM, which is enough for most 1080p gaming tasks.
- TDP (Thermal Design Power): TDP is a measurement of how much heat the GPU generates under full load. It’s an essential metric for ensuring your cooling system can handle the GPU’s heat output.
5. Compare Your Results
After you’ve completed the benchmark and reviewed the results, compare your GPU’s performance to others. If you are using UserBenchmark or Passmark, you can easily compare your GPU’s performance score to other users’ GPUs. This helps you understand where your GPU stands in terms of overall power.
You can also perform side-by-side GPU comparisons between similar models, such as comparing the RTX 3060 against the RX 6600. For this, make sure you’re comparing the same test conditions, such as resolution, settings, and workload, to get an accurate picture of their relative performance.
6. GPU Optimization and Overclocking
After benchmarking, you may want to optimize your GPU’s performance. Overclocking is one of the most common methods for boosting GPU performance.
- What is Overclocking?: Overclocking is the process of increasing the GPU’s clock speeds beyond the factory settings to improve performance. This can be done using software like MSI Afterburner or EVGA Precision X1.
- How to Overclock Your GPU: Overclocking should be done carefully, as it can lead to higher temperatures and instability if not done properly. Gradually increase the clock speed in small increments and run stress tests after each change to ensure stability.
- Monitor Temperatures and Stability: Overclocking can lead to higher temperatures, so ensure that your cooling system is adequate. Always monitor your GPU’s temperature during overclocking to avoid overheating.
- Adjust Power Limits: Most overclocking software allows you to adjust the power limit. Increasing the power limit gives the GPU more headroom to achieve higher clock speeds.
- Check for Stability: Once you’ve overclocked your GPU, run benchmarks and stress tests to ensure that your changes have improved performance without compromising stability.
Understanding GPU Stress Tests and How They Help
What is GPU Stress Testing?

A GPU stress test is a tool used to put your graphics card under extreme load to assess its stability, cooling performance, and overall strength. While benchmarking focuses on measuring the performance of your GPU in real-world scenarios, stress testing pushes your graphics card to its limits, identifying how it behaves under heavy workloads, such as gaming at max settings or rendering complex 3D environments.
Stress testing is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your GPU, especially if you plan to overclock it. The goal is to see how your GPU handles extreme scenarios and whether it can continue running at full power without overheating or crashing. This is especially important for users who rely on GPUs for gaming, professional rendering, or computational tasks like AI model training.
Stress testing tools like FurMark and Heaven Benchmark are widely used for GPU stress tests. These tools simulate high-stress environments, pushing the GPU to its maximum performance capacity. If your GPU can handle these tests without significant temperature spikes, crashes, or thermal throttling, it’s a good indicator that it’s operating within optimal parameters.
Want to understand how to check CPU stress test results alongside your GPU stress tests? Visit thetechsmarket for tips on testing your CPU and GPU together to ensure your overall system performance is balanced.
Why Should You Stress Test Your GPU?
There are several reasons why stress testing your GPU is critical. Understanding these reasons will help you realize the importance of performing a stress test before using your GPU for demanding tasks.
1. Stability Testing
Stress testing your GPU allows you to identify stability issues, particularly after overclocking or installing new drivers. When you overclock a GPU, it is pushed beyond its factory specifications, and stress testing can help determine whether the card is still stable under heavy load. If your GPU crashes or exhibits graphical artifacts during the test, it may indicate instability.
2. Temperature Monitoring
One of the main factors that affects GPU performance is temperature. As GPUs run at full capacity, they generate heat. Stress testing helps you identify if your cooling solution is adequate. If your GPU temperature rises above safe thresholds (usually 85°C or higher), the card may throttle down its performance to prevent overheating. A well-performing GPU should maintain stable temperatures, even under load.
3. Identifying Hardware Failures
Stress testing can help identify potential hardware failures before they become critical. For instance, a GPU that is showing signs of instability during stress tests might have underlying hardware issues like faulty VRAM, power delivery problems, or a defective cooling system. By catching these issues early, you can prevent costly repairs or damage to the card.
4. Verifying New Hardware Performance
When you install a new GPU or upgrade your system, stress testing ensures that the new components work well with the rest of your system. Running stress tests and benchmarking tools like 3DMark and Passmark can help confirm whether your new graphics card is performing as expected. This is especially useful for checking if the GPU is compatible with other system components, such as CPU, RAM, and storage.
5. Checking for Overclocking Success
After overclocking your GPU, stress testing ensures that your tweaks haven’t compromised the card’s performance or stability. Overclocking increases the GPU’s clock speeds, which generates more heat. Stress testing lets you verify if the overclocked GPU runs stably under load. It also helps you fine-tune your overclocking settings to ensure that the GPU doesn’t overheat or crash during heavy use.
How to Stress Test Your GPU

Performing a GPU stress test involves a series of steps to ensure accurate results. Below, we explain how to effectively stress test your GPU and what tools to use for optimal testing.
1. Select Your Stress Test Tool
Choosing the right stress testing tool is the first step in the process. Here are the most popular tools used for GPU stress testing:
- FurMark: One of the most commonly used stress testing tools, FurMark places a significant load on your GPU by rendering complex 3D images. It helps you identify potential overheating and power issues by pushing the card to its limits. FurMark is especially effective for testing GPUs under extreme conditions.
- Heaven Benchmark: This tool is ideal for testing the graphical performance of your GPU, with a focus on 3D rendering, tessellation, and complex environments. Heaven Benchmark provides both performance benchmarks and stability tests, which help assess the card’s endurance during extended gaming or rendering sessions.
- Unigine Superposition: Similar to Heaven Benchmark, this tool stresses the GPU with complex environments and tests the card’s stability at different resolutions. It is particularly useful for benchmarking high-end GPUs and checking their performance across a wide range of workloads.
- 3DMark: A versatile benchmarking tool that can be used for both stress testing and performance benchmarking. 3DMark provides various tests like Time Spy and Fire Strike, specifically designed to evaluate the capabilities of both AMD and Nvidia GPUs under extreme conditions.
2. Prepare Your System
Before running any stress test, ensure that your system is ready for testing:
- Update Drivers: Make sure your GPU drivers are up to date, as outdated drivers can lead to inaccurate test results.
- Close Background Applications: Stress testing can consume a lot of system resources, so it’s essential to close unnecessary background programs that may interfere with the test.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use software like MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z to track the temperature and utilization of your GPU during the test. This will allow you to monitor how the GPU is performing in real-time and help identify thermal issues.
- Ensure Proper Cooling: Check that your GPU cooling system (fans or liquid cooling) is functioning properly. A good cooling solution ensures that your GPU can handle the stress test without overheating.
3. Run the Stress Test
Now it’s time to start the stress test. Launch your chosen stress test tool and let it run for an extended period (typically 15-30 minutes or more). Make sure to monitor the GPU’s performance, temperature, and power consumption throughout the test. You’ll want to look for any signs of instability or thermal throttling.
4. Analyze the Results
After completing the stress test, evaluate the results to identify any potential issues:
- Frame Rates: If you are using a stress test that provides FPS data (like Heaven Benchmark or 3DMark), check the frame rates to ensure that the GPU can handle demanding workloads without dropping frames or causing performance issues.
- Temperature: The GPU temperature is one of the most crucial factors to monitor during stress testing. Temperatures above 85°C can indicate poor cooling or thermal throttling. If your GPU temperature spikes too high, you may need to improve your cooling setup or consider reducing the GPU load.
- Stability: Watch for crashes, graphical glitches, or artifacts during the stress test. These are signs of GPU instability, which could indicate that the card is underperforming or malfunctioning.
- Power Consumption: Check the power consumption of your GPU during the test. A sudden drop in power or spikes in consumption can indicate a hardware issue or inefficiency in the power supply.
5. Optimize Based on Results
If you encounter issues like high temperatures, instability, or performance drops, take steps to optimize your system:
- Improve Cooling: Upgrade your GPU’s cooling system by adding better fans or even liquid cooling.
- Underclock or Overclock: Adjust the clock speeds of your GPU based on the results. If your GPU is overheating or unstable at higher clock speeds, try lowering them slightly for better stability. If it’s running well below its potential, you may try overclocking to push its performance further.
- Adjust Power Settings: Use tools like MSI Afterburner to increase the power limit if you’re overclocking. This will allow your GPU to reach higher frequencies without throttling due to insufficient power.
GPU Benchmarks and Their Role in Performance Evaluation
What are GPU Benchmarks?

GPU benchmarking is the process of evaluating the performance of a graphics processing unit (GPU) by subjecting it to a series of tests under varying loads. These tests simulate real-world gaming and graphics-rendering scenarios to measure the GPU’s capabilities. Benchmarks provide numerical scores, frame rates, and other performance metrics that can be compared to other GPUs, helping consumers make informed decisions when purchasing or upgrading their graphics hardware.
Benchmarks are essential for gamers, content creators, and professionals who rely on GPUs for tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and machine learning. By using standardized testing tools, benchmarks can accurately reflect the GPU’s power, efficiency, and reliability. For users looking to purchase a new GPU in 2025, comparing GPU benchmarks ensures they select the most appropriate hardware based on their needs, whether for gaming, productivity, or specialized applications.
The main purpose of GPU benchmarking is to provide insights into how well a particular GPU handles various workloads, such as 3D rendering, gaming, and high-performance computing tasks. Benchmarks also allow users to compare GPUs in terms of FPS (frames per second), memory bandwidth, clock speeds, and power consumption, among other key performance indicators.
Key GPU Benchmarking Tools
To evaluate GPU performance accurately, several benchmark tools are widely used by professionals and enthusiasts. These tools simulate demanding tasks and measure how the GPU handles them. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most popular benchmarking tools:
1. 3DMark: The Industry Standard
One of the most widely used benchmarking tools is 3DMark. It’s designed to test the GPU’s performance across a variety of scenarios. 3DMark includes several benchmark tests, such as Time Spy, Fire Strike, and Sky Diver, each targeting different types of hardware and usage.
- Time Spy: This test is specifically built for DirectX 12 gaming and is ideal for high-end GPUs. It simulates a complex 3D gaming environment to measure the GPU’s performance in extreme scenarios.
- Fire Strike: This benchmark tests the GPU’s ability to handle demanding 3D games at Ultra HD (4K) settings. It’s one of the most popular tests for gamers looking to compare GPUs for high-resolution gaming.
- Sky Diver: A lighter benchmark that’s perfect for mid-range GPUs, Sky Diver simulates less demanding 3D scenarios, making it ideal for users with entry-level to mid-range graphics cards.
Using 3DMark allows users to compare their GPU’s score with others in the same price range, making it a reliable tool for benchmarking in 2025. It is essential for anyone seeking detailed insights into their GPU’s performance.
2. Heaven Benchmark: Advanced Graphics Testing
Heaven Benchmark is another widely recognized GPU benchmarking tool that tests OpenGL performance. This tool stresses the GPU by rendering complex 3D environments with advanced visual effects like tessellation, dynamic lighting, and reflections. Heaven Benchmark is great for testing high-end GPUs and provides metrics like FPS, min/max frame rates, and temperature readings.
The benchmark is available in several settings, allowing users to test performance at different resolutions and quality levels. It’s also one of the preferred benchmarks for Nvidia and AMD GPU comparisons.
- OpenGL Performance: Since Heaven Benchmark uses OpenGL, it is ideal for users with GPUs that excel in OpenGL rendering tasks, such as certain professional graphics cards or older systems.
3. FurMark: Stress Test for Stability
While primarily a stress test, FurMark is also used to benchmark GPUs by placing them under extreme loads. It is particularly useful for users who want to assess the thermal and power limits of their GPU. By running a demanding graphical workload, FurMark can help identify issues with cooling and power delivery.
FurMark is an essential tool for determining whether a GPU can sustain its performance under prolonged stress without overheating or throttling. It’s also widely used in overclocking communities to test the stability of GPUs after tuning clock speeds and voltage.
4. PassMark GPU Test: Real-World Performance Metrics
PassMark is a benchmark tool that evaluates the overall performance of a GPU using various tests that simulate real-world gaming and graphics workloads. It provides scores for 2D and 3D rendering, as well as GPU compute tasks, making it ideal for users who rely on their GPU for both gaming and productivity.
The PassMark GPU benchmark tests a wide range of GPUs, from low-end cards to the most powerful professional cards, providing detailed insights into their performance across different tasks. It is also widely used by professional reviewers and in industry standard tests.
How to Read GPU Benchmark Results
After running a GPU benchmark, it’s essential to interpret the results correctly to understand how your GPU performs. Here are the primary metrics that are usually reported in GPU benchmark tests:
1. Frames Per Second (FPS)
One of the most critical metrics in GPU benchmarking is FPS, which measures how many frames the GPU can render per second. Higher FPS translates to smoother gameplay or rendering, while lower FPS results in stuttering or lag.
- 60 FPS is generally considered the baseline for smooth gaming at 1080p.
- 120 FPS or higher is ideal for users looking to game at higher resolutions or use VR headsets that require higher frame rates for smooth performance.
2. Frame Time
Frame time refers to the amount of time it takes for the GPU to render a single frame. Lower frame times indicate that the GPU can render frames more efficiently, resulting in smoother experiences during gaming or 3D rendering tasks.
3. Power Consumption
Power consumption is another critical factor, particularly for users concerned with efficiency. Benchmark tools typically report how much power the GPU consumes during the test. A more efficient GPU will consume less power for the same level of performance.
4. Temperature
Temperature is a crucial aspect of GPU performance. If the GPU exceeds a certain temperature threshold, it may begin to throttle its performance to avoid overheating. Most benchmarking tools, like FurMark and Heaven Benchmark, track the maximum temperature reached during testing.
- Ideal Temperature Range: Most GPUs operate optimally between 60°C and 85°C. Temperatures above 90°C can indicate poor cooling and potential thermal throttling.
5. VRAM Usage
VRAM (video random access memory) is the memory that the GPU uses to store textures, shaders, and other data necessary for rendering. Benchmark tests will show how much VRAM is being used during testing. Higher-end games and applications typically require more VRAM for higher texture resolutions and complex scenes.
6. GPU Score Comparison
Benchmarking tools provide a score that represents the overall performance of your GPU. These scores are often compared against industry averages or similar GPUs to evaluate how well the card performs relative to others in its class.
GPU Comparison: Comparing Different Models

Once you’ve benchmarked your GPU, it’s time to compare it to other models. This is where the GPU comparison becomes essential, especially when upgrading your hardware or choosing between multiple GPUs for your system. Popular tools like UserBenchmark allow you to directly compare the performance of different GPUs by providing an overall performance score.
Here are a few comparisons that might help you decide between different GPUs in 2025:
1. Nvidia vs AMD GPUs
When comparing Nvidia and AMD GPUs, the two brands have their unique strengths and weaknesses. Nvidia’s RTX series cards tend to perform better in real-time ray tracing, while AMD GPUs, such as the RX 6000 series, offer excellent performance for the price, especially when paired with AMD Ryzen processors.
2. GeForce GTX 1650 vs 1660 Super
For entry-level gaming, the GTX 1650 and GTX 1660 Super are often compared. The 1660 Super offers better performance, especially for 1080p gaming, with more VRAM and higher clock speeds.
3. RTX 3060 vs RTX 3070
If you’re considering a mid-range to high-end GPU, comparing the RTX 3060 and RTX 3070 will show you that while the 3070 offers better 4K gaming performance and higher VRAM, the 3060 is a great choice for users looking to game at 1440p or 1080p resolutions.
4. Nvidia Quadro vs GeForce
For professionals, comparing the Nvidia Quadro series with the GeForce series is essential. The Quadro cards are designed for workstations, providing superior performance in CAD, 3D modeling, and video editing, while the GeForce cards are optimized for gaming and consumer-grade applications.
GPU Performance Optimization and Overclocking
Introduction to GPU Optimization

Optimizing your GPU performance is crucial for achieving smooth gameplay, higher frame rates, and efficient rendering. Whether you’re gaming, creating content, or using your PC for productivity, the GPU is one of the most important components of your system. To get the best performance out of your graphics card, you must optimize its settings, including overclocking, thermal management, and power efficiency.
While some users opt for pre-configured systems with optimized settings, others may want to fine-tune their GPU to extract the most power out of it. In this part, we will cover the key aspects of GPU performance optimization, including overclocking, cooling, and power settings.
1. Overclocking Your GPU
Overclocking involves increasing the clock speeds of your GPU beyond the manufacturer’s specifications to achieve higher performance. By adjusting these speeds, you can boost your frame rates in games, reduce rendering times in creative applications, and generally get more out of your hardware. However, overclocking also increases power consumption and generates more heat, which requires better cooling solutions.
What is Overclocking?
Overclocking the GPU means adjusting the core clock and memory clock speeds. These settings control how fast the GPU’s processor and memory operate. By pushing these limits, you can increase the overall performance of the GPU in terms of FPS (frames per second), frame times, and rendering efficiency. Overclocking is often used by gamers and content creators looking to squeeze extra performance out of their graphics cards.
How to Overclock Your GPU
The process of overclocking involves several tools and steps:
- Tools: The most popular tools for GPU overclocking include MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and NVIDIA GeForce Experience (for Nvidia GPUs). These programs allow users to adjust clock speeds, voltages, and fan speeds, monitor temperatures, and even create custom overclocking profiles.
- Core Clock and Memory Clock: Start by adjusting the core clock first. This is the speed at which the GPU processor operates. Gradually increase the clock speed in small increments (e.g., 10 MHz) and test stability using benchmark tests like 3DMark or Unigine Heaven. Once the core clock reaches a point where the performance increases and plateaus, move on to the memory clock, which affects VRAM speeds.
- Voltage: For stable overclocking, you may need to increase the voltage slightly. However, raising the voltage too high can cause excessive heat, so it’s crucial to monitor the GPU temperature during this process.
Stability Testing
Once the overclocking adjustments are made, run stability tests to ensure the GPU operates correctly without crashing. Popular stability tests like FurMark and 3DMark simulate heavy loads on the GPU, stressing it to see if the system is stable.
- FurMark: FurMark is often used for GPU stress testing and overclocking. By running FurMark, users can determine if their overclocked GPU can handle extreme conditions without crashing. If the GPU crashes or shows graphical artifacts, reduce the clock speeds and test again.
- Temperature Monitoring: During overclocking, the temperature of your GPU can rise quickly. Tools like MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor will allow you to monitor the temperature while overclocking. Ideally, the temperature should remain below 85°C for long-term reliability.
Overclocking Risks
While overclocking provides improved performance, it also comes with certain risks. If the GPU is overclocked too much, it can cause the hardware to become unstable, resulting in crashes or system failures. Furthermore, excessive overclocking can void the warranty and may reduce the lifespan of the GPU due to increased wear from higher temperatures.
2. Cooling Solutions for Optimal Performance
As the GPU works harder during overclocking or demanding tasks like gaming or 3D rendering, its temperature can increase significantly. Efficient cooling solutions are crucial to maintaining optimal GPU performance and preventing thermal throttling.
Thermal Throttling and How to Avoid It
Thermal throttling occurs when the GPU temperature exceeds safe limits, causing the GPU to slow down to avoid overheating. This can result in lower frame rates, higher frame times, and unstable performance. To avoid thermal throttling, it’s essential to have effective cooling systems in place.
Cooling Methods
- Air Cooling: The most common method of GPU cooling is through air cooling. Graphics cards typically come with built-in fans that help dissipate heat. These fans pull air through the heatsinks and expel it away from the GPU.
- Aftermarket GPU Coolers: For users seeking more effective cooling, aftermarket coolers or liquid cooling solutions can significantly improve temperature management. Brands like NZXT, Corsair, and EVGA offer high-performance cooling systems for GPUs, often featuring larger radiators or more powerful fans.
- Case Airflow: Ensuring that the entire PC case has good airflow is another important factor in keeping the GPU cool. Installing additional case fans and optimizing their placement can enhance airflow and prevent the GPU from overheating.
Monitoring Temperatures
To keep track of the GPU’s health and avoid thermal throttling, monitor the temperatures using tools like MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor. Setting temperature thresholds within these tools will help you receive alerts if the GPU temperature reaches dangerous levels.
3. Power Management and Efficiency
Optimizing GPU power settings is another crucial aspect of overall performance optimization. While overclocking and maximizing performance are key for users who prioritize performance, power management ensures that the GPU runs efficiently, avoiding unnecessary power consumption while maintaining stable performance.
Power Limit Adjustment
Most modern GPUs have a power limit setting, which allows users to control the amount of power the GPU draws during operation. By adjusting this setting, users can prevent the GPU from drawing more power than needed, especially in situations where performance isn’t a priority. This is useful in scenarios where you want to reduce energy consumption or extend the lifespan of your GPU.
GPU Power Consumption
Power consumption is an important factor for users who care about system efficiency and power costs. GPUs with higher performance typically consume more power, especially when running demanding tasks or overclocked. Tools like MSI Afterburner allow you to monitor power consumption and adjust settings accordingly.
Voltage Control
Voltage control allows users to fine-tune their GPUs’ power delivery. Under-volting is a process where the user reduces the voltage supplied to the GPU while keeping the performance stable. This can lead to lower power consumption and heat generation, making it ideal for users who want to increase their GPU’s efficiency without sacrificing much performance.
4. Software Settings for Optimization
Aside from hardware adjustments, several software settings can help improve GPU performance:
- Driver Updates: Keeping your GPU drivers up-to-date ensures you are getting the best performance optimizations, bug fixes, and compatibility improvements from the GPU manufacturer. Regularly check the GPU manufacturer’s website (Nvidia or AMD) for driver updates.
- Game Settings: Adjusting the in-game settings for higher FPS or better visual quality is another way to improve GPU performance. By reducing the game’s graphics settings, such as shadow quality, texture resolution, and anti-aliasing, users can achieve higher frame rates and smoother performance.
- Nvidia Control Panel/AMD Radeon Settings: Both Nvidia and AMD provide control panels where users can optimize graphics settings for performance. This includes adjusting options like V-Sync, frame rate limits, and anti-aliasing to find the best balance between quality and performance.
5. Monitoring GPU Performance Over Time
To maintain optimal performance, it’s essential to monitor the GPU regularly, especially during intense tasks like gaming or content creation. Tools like UserBenchmark, GPU-Z, and HWMonitor allow you to track real-time GPU performance, temperature, power consumption, and clock speeds.
Performance Degradation
Over time, the performance of a GPU may degrade due to various factors such as overheating, dust buildup, or wear and tear on the hardware. Regular maintenance, cleaning, and thermal monitoring can help extend the GPU’s lifespan.
GPU Performance Comparison – Nvidia vs. AMD
Introduction to GPU Comparison
When selecting a graphics card, two major players dominate the market: Nvidia and AMD. Both companies offer high-performance GPUs, but they differ in technology, performance, and price points. Whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or professional, understanding the differences between Nvidia and AMD graphics cards can help you make an informed decision based on your needs.
In this section, we will compare the two companies’ graphics cards in several categories, including performance, price, features, and power efficiency. Additionally, we will look at specific models from each company, such as the Nvidia GeForce RTX 3070 and the AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT, to help you understand how these GPUs stack up against each other in real-world applications.
1. Performance Comparison: Nvidia vs. AMD

Both Nvidia and AMD offer high-end GPUs that cater to gamers and professionals looking for exceptional performance. The performance of a GPU is generally measured in frames per second (FPS), rendering speed, and graphical fidelity.
Nvidia GeForce RTX Series:
Nvidia’s RTX 3000 series and the newer RTX 4000 series GPUs are designed for demanding gaming and 3D rendering. These GPUs include Tensor cores for AI-based tasks and Ray Tracing cores that provide real-time ray tracing for enhanced visual effects. The RTX 3070 and RTX 3080 are known for delivering high FPS rates in 4K gaming and high-definition rendering. Nvidia’s DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) technology uses AI to boost performance by rendering fewer pixels and upscaling the image, providing smoother gameplay without sacrificing visual quality.
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 3070: Known for its incredible 4K gaming performance, the RTX 3070 offers performance that is close to the RTX 2080 Ti, but at a significantly lower price point. It delivers up to 144 FPS in 1440p gaming and is capable of handling demanding tasks like video rendering and AI-based workloads.
AMD Radeon RX Series:
AMD’s Radeon RX 6000 series, based on the RDNA 2 architecture, is a direct competitor to Nvidia’s RTX series. AMD focuses on raw performance and price-to-performance ratio while offering Ray Tracing features with its RX 6800 XT and RX 6700 XT models. Although AMD’s ray tracing performance isn’t as powerful as Nvidia’s, it offers excellent value for money in traditional rasterization tasks.
- AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT: A competitor to Nvidia’s RTX 3070, the RX 6700 XT excels in 1440p gaming and is a great choice for those looking for excellent performance at a mid-range price. It provides high FPS in modern games but falls behind Nvidia’s ray tracing performance due to the lack of advanced hardware like Tensor cores.
2. Ray Tracing Performance
Ray tracing is one of the most significant advancements in modern GPU technology, offering more realistic lighting, shadows, and reflections in games and simulations. Nvidia’s RTX series GPUs were the first to feature real-time ray tracing, thanks to their RT cores. In contrast, AMD’s RDNA 2 architecture now includes ray tracing capabilities, but they don’t quite match Nvidia’s performance in this area.
Nvidia Ray Tracing:
Nvidia has built its reputation on Ray Tracing technology with its RTX series. The RTX 3000 series and the latest RTX 4000 series GPUs come with dedicated RT cores that accelerate real-time ray tracing, providing lifelike visuals and more immersive gaming experiences. While the RTX 3060 and RTX 3070 perform well at 1440p with ray tracing, the RTX 3080 and RTX 3090 handle 4K ray tracing at smooth frame rates, making them ideal for high-end gaming and content creation.
AMD Ray Tracing:
AMD’s RX 6000 series GPUs also offer ray tracing, but with less impressive results compared to Nvidia. The RX 6800 XT and RX 6700 XT can handle ray-traced visuals, but they fall behind in terms of performance per watt and image quality when compared to Nvidia’s RTX 3000 series. AMD uses Compute Units instead of dedicated RT cores, which leads to less efficient ray tracing performance, especially at higher resolutions.
3. Power Efficiency and Temperature Control
One of the key factors when choosing a GPU is power consumption. More powerful GPUs tend to consume more power and generate more heat, which can impact system stability and cooling.
Nvidia’s Power Efficiency:
Nvidia’s RTX 3000 series GPUs, thanks to Ampere architecture, offer a good balance of power efficiency and performance. These GPUs provide higher performance per watt than the previous Turing architecture (RTX 20xx series), which reduces power draw during heavy workloads. Additionally, Nvidia has refined its DLSS and ray tracing technologies to ensure minimal power consumption while still providing exceptional gaming performance.
- RTX 3070: This GPU draws about 220 watts, which is relatively low for its performance level. Its power efficiency allows users to run demanding applications and games while maintaining lower temperatures, even under load.
AMD’s Power Efficiency:
AMD’s RDNA 2 architecture in the RX 6000 series has improved in terms of power efficiency when compared to the older GCN architecture in previous AMD GPUs. The RX 6700 XT draws about 230 watts, which is a reasonable power draw for its mid-range performance. However, the RX 6800 XT can draw 300 watts under load, which can result in higher temperatures and the need for more robust cooling systems.
- RX 6800 XT: While the RX 6800 XT performs well at 1440p and even 4K, its power consumption and thermal management aren’t as optimized as Nvidia’s latest offerings. AMD GPUs tend to run a bit hotter under heavy load, which could require additional cooling solutions.
4. Price-to-Performance Ratio
One of the most important considerations for consumers is the price-to-performance ratio. In general, AMD is known for offering better value for money, especially in the mid-range market. Nvidia, on the other hand, tends to have higher prices due to its cutting-edge technology, like DLSS, ray tracing, and AI-based features.
Nvidia’s Pricing Structure:
Nvidia’s RTX 3000 series GPUs, including the RTX 3070 and RTX 3080, offer great performance for enthusiasts, but they come at a premium. The RTX 3070 is priced higher than the RX 6700 XT, but it provides better ray tracing performance and 4K gaming capabilities. The RTX 3080 and RTX 3090 are geared toward those who need exceptional rendering performance for content creation, VR, and AI workloads.
AMD’s Pricing Strategy:
AMD’s RX 6700 XT offers similar performance to the RTX 3070 but at a more affordable price point, making it an attractive choice for budget-conscious gamers. The RX 6800 XT is also competitively priced, offering performance close to Nvidia’s RTX 3080, but at a lower cost. AMD’s RX 6000 series offers a strong price-to-performance ratio for gamers who are not as concerned with ray tracing or DLSS.
5. Software Features and Ecosystem
Both Nvidia and AMD offer their own set of software features and ecosystems that enhance the GPU experience.
Nvidia’s Software Features:
- Nvidia GeForce Experience: A suite of tools that help optimize game settings, capture gameplay, and share videos. GeForce Experience also provides driver updates and allows for automatic optimizations.
- Nvidia Broadcast: A streaming platform that uses AI to improve audio and video quality, providing noise removal, background blur, and virtual green screen features.
- Nvidia Reflex: A technology designed to reduce system latency, ideal for competitive gamers.
AMD’s Software Features:
- AMD Radeon Software: This software suite offers features such as Radeon Boost, Radeon Chill, and Radeon Anti-Lag. AMD’s software has significantly improved in recent years, offering optimization tools, driver updates, and game tuning.
- Radeon RX 6000 Features: AMD’s FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR) is AMD’s answer to DLSS, providing upscaling to improve game performance while maintaining visual quality.
Best GPU Options in 2025

Final GPU Selection
As we conclude our deep dive into the world of GPUs, we have explored a range of factors that influence your decision when choosing between Nvidia and AMD graphics cards. From performance and ray tracing capabilities to power efficiency, price-to-performance ratio, and software ecosystem, it’s clear that the right GPU depends on your specific needs, budget, and intended use.
In this final section, we’ll summarize the key takeaways from our comparison and guide you in selecting the best GPU for your needs in 2025. Whether you’re a gamer, content creator, or professional, this section will help you make the most informed decision.
1. Overview of Key Factors
To recap, when selecting a GPU, there are several key factors to consider:
- Performance: This includes frames per second (FPS), rendering speed, and the ability to handle high-resolution gaming or complex graphical tasks. If you need a GPU for 4K gaming or VR, high-end options like the RTX 4080 or RX 6900 XT should be your focus. For 1440p gaming, the RTX 3070 or RX 6700 XT offers a great balance of price and performance.
- Ray Tracing: If you’re interested in real-time ray tracing, Nvidia’s RTX series is the top choice, thanks to its dedicated RT cores and DLSS technology. For those who prioritize raw performance over visual enhancements, AMD’s RX series still performs well but may lag in ray tracing-heavy games.
- Price-to-Performance Ratio: Nvidia’s RTX cards tend to be on the pricier side, especially the higher-end models like the RTX 3080 and RTX 3090. AMD’s RX 6000 series, however, provides better value for the price, offering strong performance at a lower cost.
- Software Ecosystem: Nvidia’s GeForce Experience and DLSS technology give it an edge for those using AI-based applications and looking for a polished experience. Meanwhile, AMD’s Radeon Software suite provides robust optimization and FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution) for competitive gamers.
2. Best GPU for Gaming in 2025

If gaming is your primary concern, choosing the right GPU can significantly impact your overall experience. Here’s a breakdown of the best gaming GPUs in 2025.
Learn more about screen resolutions and how your choice of resolution can impact your overall gaming experience and GPU requirements.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4080 and 4090
For enthusiast-level gaming, the RTX 4080 and RTX 4090 are the undisputed leaders. Offering exceptional ray tracing, 4K gaming performance, and AI-based enhancements, these GPUs are ideal for those who want to experience immersive gameplay with stunning visual effects. The RTX 4090 delivers the best performance available, making it perfect for gamers looking to run heavy titles at high FPS.
- Pros: Best performance for 4K gaming, advanced ray tracing, DLSS technology, and future-proof for upcoming titles.
- Cons: Expensive, power-hungry.
AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT
On the AMD side, the Radeon RX 6900 XT competes with the RTX 3080 and RTX 3090, offering great value for money in the high-end gaming segment. While it may lack the same ray tracing capabilities as Nvidia, the RX 6900 XT excels in raw rasterization performance, making it an excellent choice for 1440p gaming and even 4K gaming at high settings.
- Pros: Excellent price-to-performance ratio, strong 1440p gaming and 4K gaming performance, competitive with Nvidia’s RTX 3080.
- Cons: Lower ray tracing performance, lacks DLSS.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3070 and 3070 Ti
For mid-range gaming, the RTX 3070 and RTX 3070 Ti are solid choices, providing fantastic 1440p performance and capable 4K gaming. With ray tracing and DLSS, these GPUs offer a strong balance of price and performance, making them ideal for gamers who want next-gen features at a more affordable price.
- Pros: Great 1440p gaming performance, supports ray tracing and DLSS, excellent for high refresh rates.
- Cons: Higher price compared to AMD alternatives like the RX 6700 XT.
AMD Radeon RX 6700 XT
The RX 6700 XT is one of the best GPUs for 1440p gaming, competing directly with the RTX 3070. It delivers excellent price-to-performance, offering solid gaming performance with good power efficiency. However, it lacks the ray tracing power of Nvidia’s RTX series but excels in traditional rasterized performance, making it a great option for gamers who don’t need the latest ray tracing features.
- Pros: Fantastic value for money, excellent 1440p performance, competitive with RTX 3070.
- Cons: Limited ray tracing performance, lacks DLSS.
3. Best GPU for Content Creation and Professional Workloads

When it comes to content creation, tasks like video rendering, 3D modeling, and AI-based work require GPUs that offer high compute performance. Here are the best GPUs for professionals in 2025.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 4090 (for Content Creators)
The RTX 4090 is the best GPU for content creators. With its incredible CUDA cores, Tensor cores, and Ray Tracing cores, it provides fast rendering speeds for 3D modeling, video editing, and AI-driven applications. Whether you’re working in Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, or Autodesk Maya, the RTX 4090 will make your workflows smoother and more efficient.
- Pros: Best GPU for professional workloads, excellent for video editing, AI, and 3D rendering.
- Cons: Extremely expensive, requires a robust power supply.
AMD Radeon Pro W6800
The AMD Radeon Pro W6800 is built for workstations and is a strong alternative to Nvidia’s Quadro series. It provides exceptional performance in 3D rendering, content creation, and CAD applications. While not as powerful as Nvidia’s RTX 6000 series, the W6800 provides great value for those on a budget.
- Pros: Great performance in workstation tasks, competitive pricing.
- Cons: Lower ray tracing and AI performance compared to Nvidia.
4. Best GPU for Budget Gamers in 2025

If you’re on a budget but still want a GPU capable of handling modern games, there are several great options in 2025 that offer excellent performance without breaking the bank.
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1660 Super
For budget gamers, the GTX 1660 Super provides great 1080p gaming performance at an affordable price. While it lacks ray tracing and DLSS, it offers great performance in non-ray traced games, making it ideal for gamers who don’t mind missing out on the latest visual effects but still want smooth gameplay.
- Pros: Excellent 1080p gaming performance, affordable.
- Cons: No ray tracing or DLSS.
AMD Radeon RX 6600 XT
The RX 6600 XT offers solid 1080p gaming performance and competes directly with Nvidia’s GTX 1660 Super and RTX 3050. It provides great value for money, offering fast rendering and competitive FPS rates in modern titles, though it lacks ray tracing and AI features.
- Pros: Fantastic value for 1080p gaming, excellent price-to-performance ratio.
- Cons: Lacks ray tracing and DLSS.
Which GPU Should You Choose in 2025?
Selecting the right GPU in 2025 depends on your specific use case, whether you are gaming, creating content, or running professional workloads. If you prioritize ray tracing and AI features, Nvidia’s RTX series is the best option. For gamers looking for great performance at a reasonable price, AMD’s RX 6000 series offers excellent alternatives.
Ultimately, whether you’re seeking top-tier gaming performance or workstation-ready GPUs, there’s a perfect choice for you in 2025. With new models, improved technologies, and price reductions on older GPUs, this year offers some of the best value in graphics card technology yet.
Conclusion
As we wrap up this comprehensive guide to the best GPUs in 2025, it’s clear that the world of graphics cards continues to evolve rapidly, offering something for every type of user, from enthusiast gamers and content creators to budget-conscious buyers and professional users. Choosing the right graphics card requires careful consideration of various factors, including performance, price, features, and the specific tasks you plan to undertake.
Key Takeaways:
- Performance: Nvidia’s RTX 40 series dominates in terms of raw power, making it the best option for 4K gaming, ray tracing, and AI applications. On the other hand, AMD’s RX 6000 series provides a strong price-to-performance ratio, excelling in traditional rasterized graphics for 1080p and 1440p gaming.
- Ray Tracing and AI Features: Nvidia’s RTX cards, with DLSS and ray tracing support, are the go-to for gamers and professionals seeking visual realism. AMD is catching up with FSR (FidelityFX Super Resolution), but Nvidia still leads in this category.
- Value for Money: For those looking for a cost-effective option, the GTX 1660 Super and RX 6600 XT are excellent budget GPUs that provide great performance without the premium price tag of ray tracing-enabled models.
- Workstation and Content Creation: Nvidia’s RTX 4090 and Radeon Pro W6800 are tailored for content creators and professionals, offering the power needed for 3D rendering, AI-based applications, and video editing.
Final Thoughts:
- For Gaming: If you’re a gamer looking for the best visuals and performance in 2025, the RTX 4090 and RTX 4080 are the ultimate choices for high-end 4K gaming and ray tracing. However, for more affordable options, the RTX 3070 or RX 6700 XT are also excellent performers at 1440p resolution.
- For Content Creation: If you’re working on video editing, 3D modeling, or AI-driven projects, the RTX 4090 is the top-tier GPU, followed by the Radeon Pro W6800 for those who need workstation-level performance at a more budget-friendly price.
- For Budget Gamers: If your budget is tight but you still want a GPU that can handle modern games well, the GTX 1660 Super or RX 6600 XT are great options for 1080p gaming, offering a solid balance of performance and affordability.
Ultimately, the best GPU for you in 2025 depends on your specific needs and budget. The landscape is diverse, offering high-end options for power users and more affordable choices for casual gamers and professionals who don’t need the absolute best.
Looking Ahead:
As GPU technologies continue to advance, we can expect further innovations in ray tracing, AI-based rendering, and power efficiency. New generations of GPUs will bring even better performance at lower prices, making 2025 a great year to invest in a new graphics card. Whether you choose Nvidia’s cutting-edge RTX series or AMD’s RX 6000 lineup, you can rest assured that your new GPU will be a crucial part of the gaming, creation, or professional experience of the future.
FAQs
What is the #1 GPU in the world?
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 is considered the top GPU, offering the best performance for gaming and content creation.
Is FurMark a good GPU benchmark?
Yes, FurMark is a popular GPU stress test tool, but it’s intense and may cause high temperatures. Use caution when testing.
How to do a GPU stress test?
- Download stress test software like FurMark or 3DMark.
- Run the test and monitor your GPU’s temperature and performance.
- Analyze the results for stability or issues.