DDR6 RAM | What You Need to Know About the Future of Computer Memory
Upgrading a PC or building a new one often feels overwhelming, especially when it comes to choosing the right memory. With constant changes in RAM types and release timelines, many users are left wondering whether their current setup is already outdated or if it’s worth waiting for the next big leap.
That’s where DDR6 RAM enters the conversation. Designed to offer faster speeds, greater efficiency, and future-ready architecture, this upcoming memory standard promises to simplify decisions and power next-gen computing without the confusion of past upgrades.
A Brief History of DDR RAM Generations

RAM has gone through several major upgrades over the years. Each generation brought faster speeds, lower power consumption, and improved performance. Understanding when each DDR generation came out helps users compare their current memory with what’s coming next.
DDR1 was released in the early 2000s and could reach speeds up to 266 MT/s. DDR2, launched in 2003, improved on speed and efficiency, supporting up to 800 MT/s. Then came DDR3 in 2007 with 2133 MT/s support and a drop in voltage. In 2014, DDR4 entered the market, raising maximum speeds to 3200 MT/s and lowering voltage to 1.2V.
DDR5, which officially launched in 2020, pushed limits further with speeds up to 8400 MT/s and added features like dual-channel DIMMs per module. This generational timeline highlights why DDR6 is the most anticipated RAM update yet.
DDR RAM Generational Comparison
|
DDR Version |
Release Year |
Max Speed (MT/s) |
Operating Voltage |
Key Improvement |
|
DDR1 |
~2000 |
266 |
2.5V |
First DDR standard |
|
DDR2 |
2003 |
800 |
1.8V |
Faster I/O, lower power |
|
DDR3 |
2007 |
2133 |
1.5V |
Higher speed, better power |
|
DDR4 |
2014 |
3200 |
1.2V |
Enhanced efficiency |
|
DDR5 |
2020 |
8400 |
1.1V |
Dual channels per DIMM |
What Is DDR6 RAM and Why It Matters
DDR6 is the upcoming standard of computer memory designed to replace DDR5. It is being developed to handle higher bandwidth, faster speeds, and increased multitasking across future devices. Unlike past upgrades, DDR6 brings more structural changes, making it a true next-generation memory solution.
One of the main upgrades is the introduction of four memory channels per DIMM, compared to the two in DDR5. This makes it possible to send more data at once, increasing efficiency in gaming, server processing, and professional rendering tasks. Variants like LP DDR6 are expected for mobile devices, while DDR6X may target GPUs and graphics-heavy applications.
DDR6 RAM Release Date: What We Know So Far
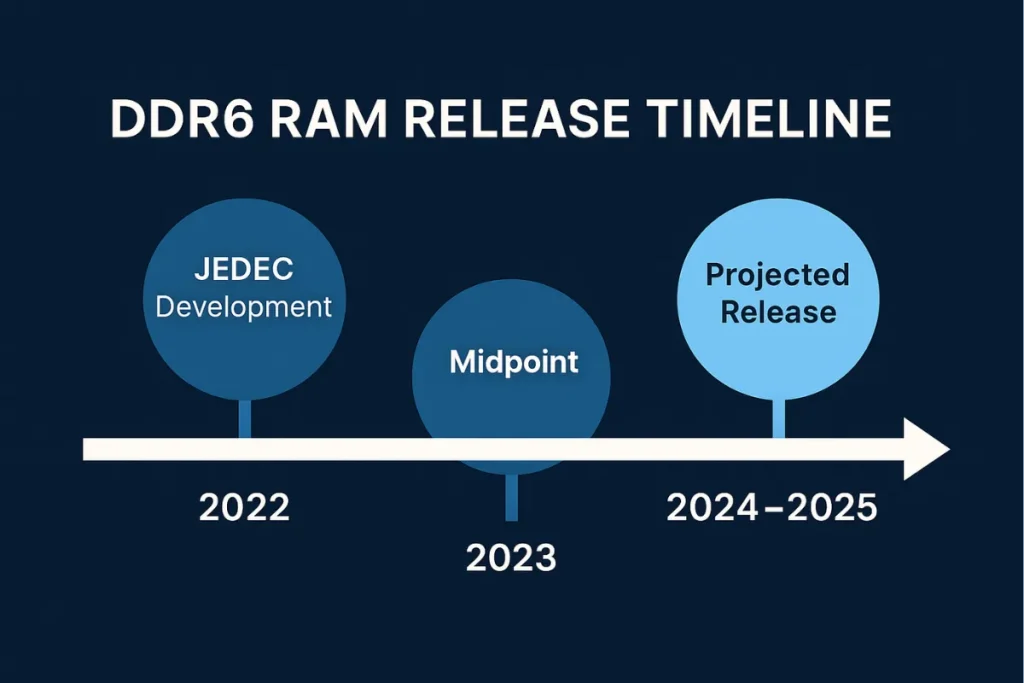
Many users want to know: When is DDR6 coming out? Industry sources indicate a likely release date in late 2024 or early 2025, depending on production schedules and chipset compatibility. Just like DDR5 RAM had a gradual rollout, DDR6 will likely start with high-end servers and trickle down to desktops and laptops.
The DDR RAM release date for each generation has historically followed a 7–8 year cycle, and DDR6 seems to follow the same pattern. While DDR5 began appearing in consumer hardware in 2021, widespread DDR6 support may take until mid or late 2025.
This upcoming standard is not yet available on shelves. However, companies have already begun testing early samples for benchmarking and stability. The rollout will depend on motherboard support and BIOS updates, just as it did with DDR4 and DDR5.
Before adopting DDR6, users will need something close to a site survey—analyzing BIOS compatibility, chipset readiness, and voltage requirements before making the switch.
DDR6 RAM Speed and Bandwidth Capabilities
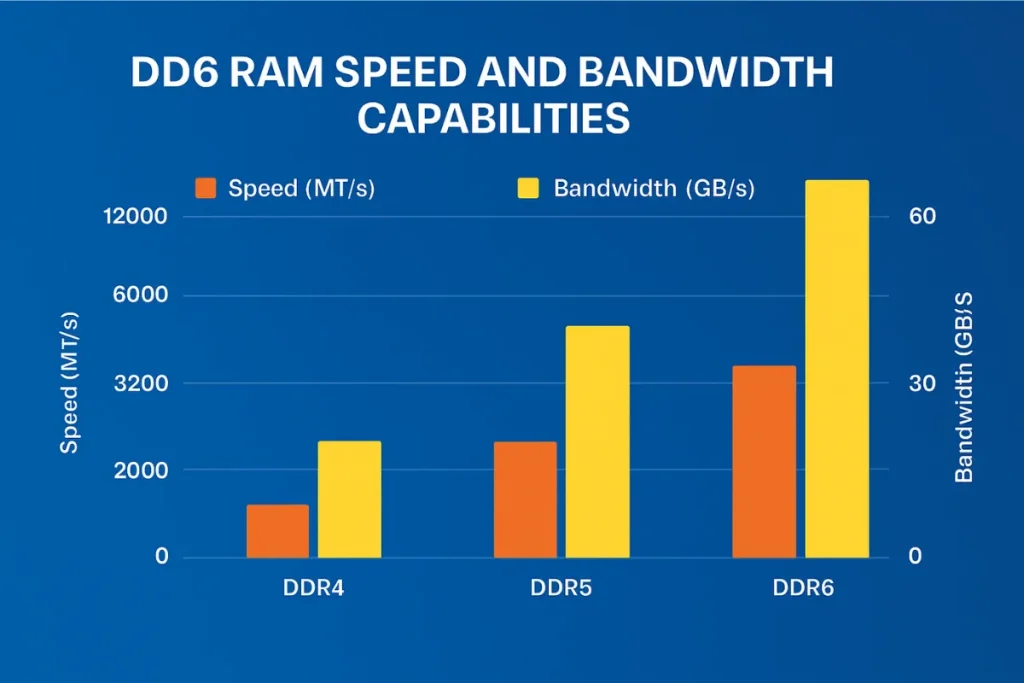
DDR6 is not just a small upgrade. It is expected to double the speed of DDR5. Initial specs show starting speeds of 12,800 MT/s, with potential to go beyond 17,000 MT/s in future revisions. This increase makes DDR6 ideal for gaming, video editing, 3D rendering, and large dataset processing.
Bandwidth will also see a big improvement. With quad-channel architecture, DDR6 can achieve bandwidth over 60 GB/s per module. This is far beyond what current DDR4 or DDR5 offers and will reduce performance bottlenecks in high-demand systems.
In terms of power efficiency, DDR6 is expected to consume even less voltage than DDR5, leading to better thermal management and increased system lifespan. These advancements make it the best choice for those planning a future-ready PC or workstation.
The leap in DDR6 bandwidth is similar to how visuals dramatically improve when moving from 1080p to 4K screen resolution—more data, faster results.
DDR6 vs DDR5: What’s the Difference?
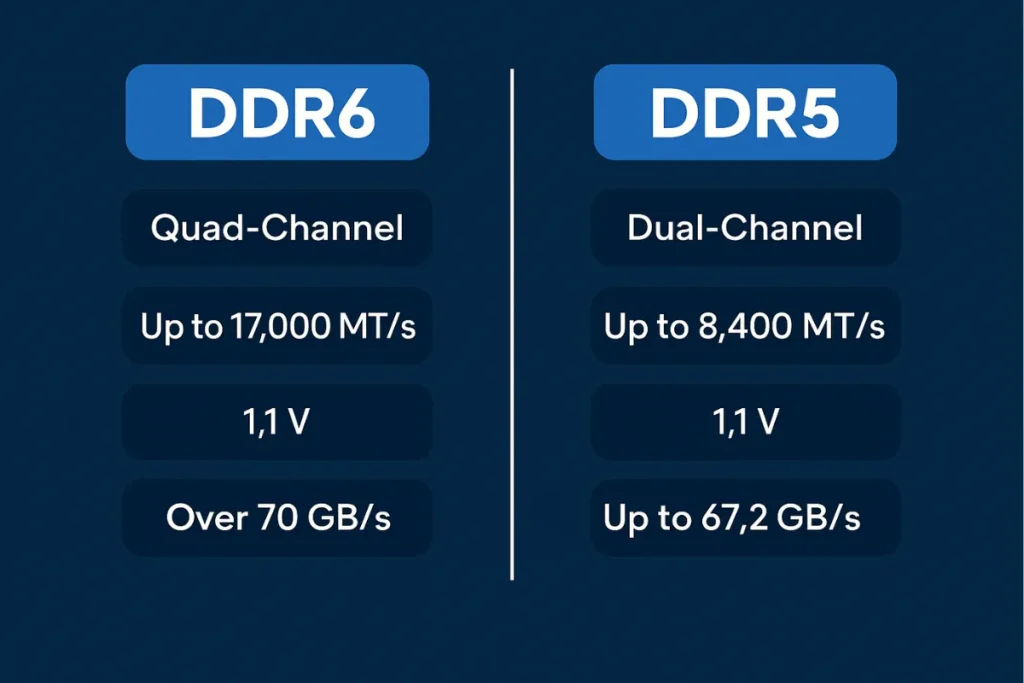
While both DDR5 and DDR6 are powerful, their internal structures and performance outputs vary significantly. The most noticeable change is the memory channel count—DDR5 supports dual channels, but DDR6 offers quad channels, making data transfer more efficient.
Power usage is another difference. DDR6 operates on lower voltage, which helps reduce heat and improves long-term durability. It also shows better latency handling, an area where DDR5 sometimes struggles in real-time tasks.
In side-by-side use, DDR6 offers nearly double the bandwidth, making it better for high-speed operations like 4K gaming, simulation, and real-time analytics. These differences justify the excitement among users comparing DDR5 vs DDR6.
Modern workloads like data validation or AI modeling demand memory that handles large-scale datasets with minimal latency—DDR6 is being designed with these tasks in mind.
DDR5 vs DDR6 Technical Specs
|
Feature |
DDR5 |
DDR6 (Projected) |
|
Max Speed (MT/s) |
Up to 8400 |
12,800+ |
|
Bandwidth per Module |
~38.4 GB/s |
60–70 GB/s |
|
Channels per DIMM |
2 |
4 |
|
Voltage |
1.1V |
<1.1V |
|
Architecture |
Dual-channel |
Quad-channel |
GDDR6 Explained: How Is It Different from DDR6?
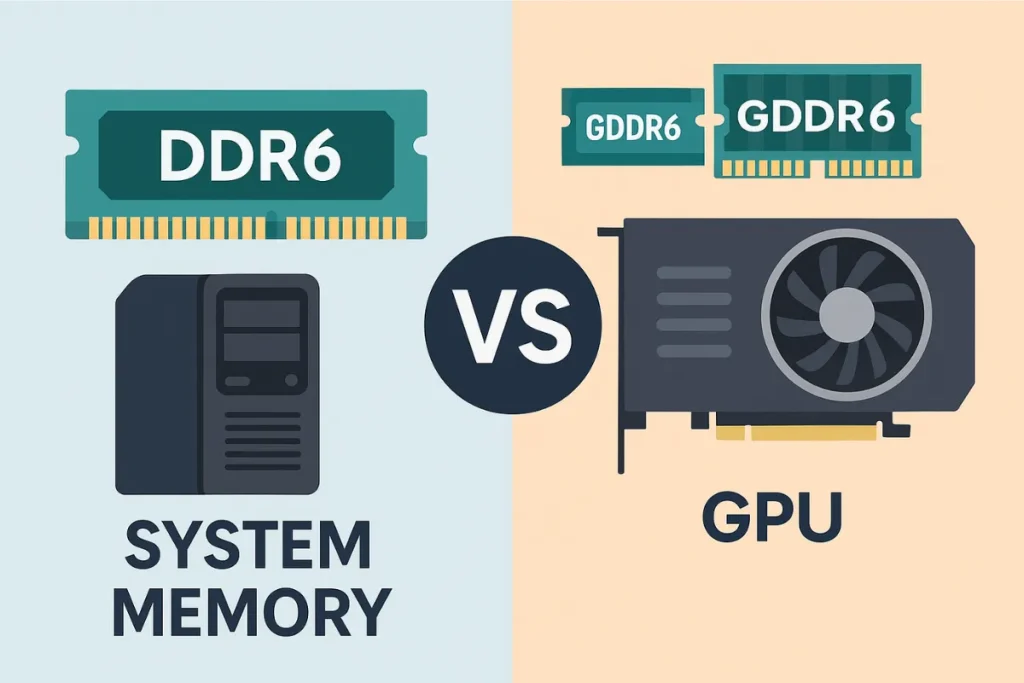
Many users confuse DDR6 RAM with GDDR6, but they are built for different purposes. GDDR6, or Graphics Double Data Rate version 6, is optimized for GPU memory, not system memory. It’s commonly found in modern graphics cards and supports high bandwidth operations crucial for rendering images, videos, and real-time game environments.
GDDR6 can reach bandwidths of up to 768 GB/s when used in multi-module configurations on GPUs. Its primary job is to communicate between the GPU and the video frame buffer, offering faster pixel data handling. On the other hand, DDR6 is general-purpose system memory intended to handle CPU operations like app execution, multitasking, and memory caching.
If you’re trying to compare GDDR6 vs DDR5 or GDDR6 vs DDR4, remember that GDDR focuses on graphics workloads, while DDR handles overall system performance. Neither replaces the other—they work side by side in modern systems.
Why GPUs Use GDDR6 but Motherboards Don’t
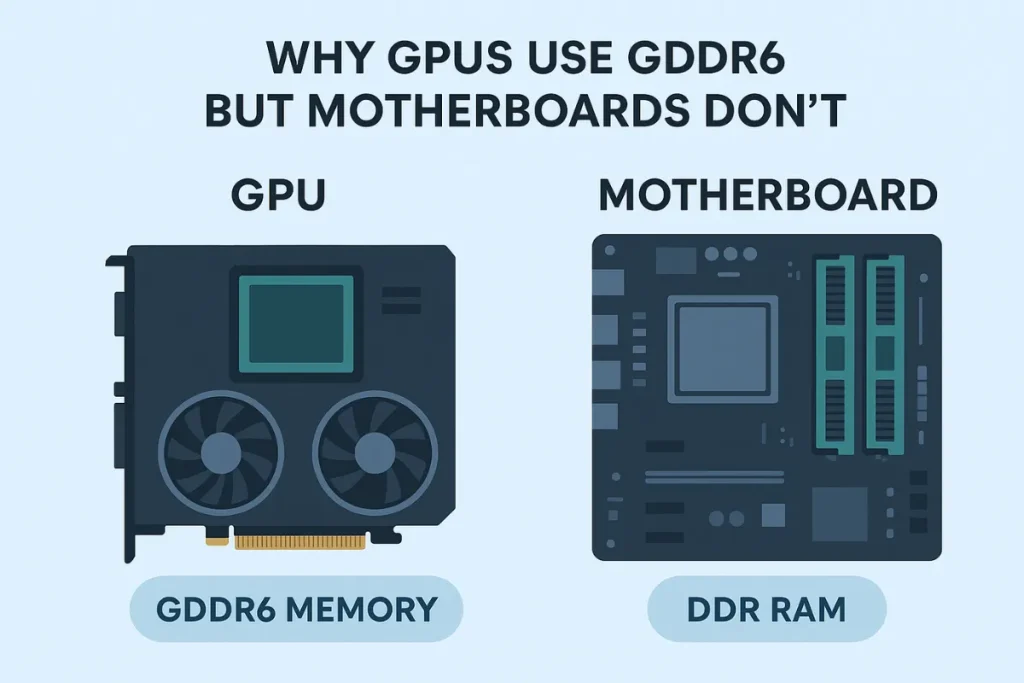
Modern GPUs use GDDR6 for a reason: it’s designed for parallel bandwidth and frame rendering. Games and video processing demand massive data transfer between video memory and the GPU core. GDDR6 handles that better than any DDR standard.
In contrast, motherboards use DDR memory because CPUs interact differently with RAM. The system memory must support multi-process workloads, maintain compatibility with BIOS and chipsets, and manage instruction sets beyond graphics.
Also, GDDR modules are soldered directly onto the GPU board, while DDR memory is installed via DIMM slots on the motherboard. That physical difference makes GDDR unsuitable for motherboards. Until DDR6 RAM is available for public use, most consumer systems will continue running DDR5 or DDR4 RAM.
Understanding how computer cords, connectors, and cables interact with internal hardware can help explain why different memory types are used across components.
DDR Memory Upgrades and Compatibility
Before upgrading to DDR6, users must verify compatibility. New RAM types usually require new motherboards with compatible chipsets. That’s because changes in voltage, timing, and channel architecture aren’t backward compatible.
So, if you’re planning an upgrade, start by checking what DDR RAM you currently have. Most modern systems display this information in the BIOS, or you can use tools like CPU-Z. It’s also important to confirm whether your motherboard supports newer RAM generations.
As DDR memory types evolve, understanding their limitations becomes essential. Users often ask, “Can I use DDR6 on a DDR5 motherboard?” The answer is no. You’ll need new hardware designed to support the features and power delivery that DDR6 demands.
Just like choosing between Cat5 vs Cat6 cables for better network performance, upgrading RAM types depends on system compatibility and bandwidth requirements.
Will DDR6 Be the Best RAM Yet?

DDR6 is being built with the future in mind. From AI model training to real-time simulations and immersive gaming, the demand for faster, more efficient RAM is only growing. The quad-channel design, lower voltage, and expanded bandwidth make DDR6 a powerful upgrade over previous memory standards.
It may not make sense for all users to switch on day one, especially with hardware and cost considerations. But once supported platforms and motherboards roll out, DDR6 RAM will likely become the preferred choice for enthusiasts, creators, and professionals.
If you’re planning to build a PC that can handle what’s next in technology, waiting for DDR6 could be a wise move. Tasks such as API integration, automated scripts, and cloud functions can benefit significantly from the improved speed and responsiveness DDR6 brings.
Comparison Table: DDR4 vs DDR5 vs DDR6
|
Feature |
DDR4 |
DDR5 |
DDR6 (Expected) |
|
Release Year |
2014 |
2020 |
2024–2025 |
|
Max Speed (MT/s) |
3200 |
8400 |
12800+ |
|
Voltage |
1.2V |
1.1V |
<1.1V |
|
Memory Channels |
1 per DIMM |
2 per DIMM |
4 per DIMM |
|
Max Bandwidth (GB/s) |
~25.6 |
~38.4 |
60–70 |
|
Main Use |
General Use |
Gaming, Desktop |
AI, Gaming, HPC |
Much like changes in Ethernet cable wiring standards over time, each new RAM generation introduces new architecture and pin arrangements that affect compatibility.
Conclusion
The development of DDR6 RAM marks a critical step in the evolution of computer memory. It’s not just about higher numbers—it’s about transforming how memory interacts with processors, GPUs, and the tasks we throw at our machines every day.
With significantly faster speeds, greater efficiency, and quad-channel architecture, DDR6 is poised to become the standard for high-performance systems. Whether you’re upgrading in the next year or planning a future build, understanding what DDR6 brings ensures you stay ahead in the ever-changing world of technology.
FAQs
Is GDDR6 better than DDR5?
GDDR6 and DDR5 serve different purposes, so one isn’t universally better than the other. GDDR6 is built for graphics cards (GPU memory) and offers extremely high bandwidth for rendering and video processing. DDR5 is used in system memory and handles general computing tasks. Each is better in its own domain.
Does DDR7 RAM exist?
No, DDR7 RAM does not exist yet. The focus is currently on finalizing and launching DDR6. DDR7 might be years away, depending on future advancements and industry demand for faster memory standards.
Is DDR5 or 6 better?
In terms of performance, DDR6 is expected to outperform DDR5. It will feature quad-channel architecture, higher bandwidth, and better efficiency. However, since DDR6 is not yet released, DDR5 remains the best available RAM standard today.
Is DDR6 RAM released?
No, DDR6 RAM has not been released for commercial use. Early development is underway, and the expected release date is around 2025. It is not yet available in stores or supported by motherboards currently on the market.
Will DDR6 RAM require a new motherboard?
Yes, like past generations, DDR6 will require a new motherboard with compatible chipsets and sockets. Memory architecture changes—like voltage, channel count, and signaling—mean older boards won’t support DDR6 modules.
When did GDDR6 come out?
GDDR6 was introduced around 2018 and became widely adopted in graphics cards like the NVIDIA RTX 20 series and AMD Radeon RX series. It replaced GDDR5 and GDDR5X as the standard for modern GPU memory.