Block Foundation vs Poured Concrete Foundation | Choose the Best for Your Home
A block foundation is a popular type of foundation used in residential and commercial construction, known for its affordability, durability, and ease of installation. It consists of concrete blocks or cinder blocks stacked to form the base of a building.
The foundation serves as the structural base for the rest of the construction, providing support and stability. This type of foundation is particularly useful for homes with basements, as it provides a solid base and excellent moisture resistance when installed properly.
However, it’s essential to compare block foundations with other foundation types like poured concrete foundations to determine the best option for your specific needs.
In this article, we’ll explore block foundations, their advantages and disadvantages, and the installation process, all while examining how they stack up against poured concrete foundations.
What is a Block Foundation?

A block foundation is a type of foundation made from stacked concrete blocks or cinder blocks. These blocks are typically hollow or solid, and they are used to create a durable and stable base for a building. Concrete blocks are made of cement and aggregates, which are mixed and then molded into rectangular shapes. The primary function of a block foundation is to support the structure above it, transferring the load to the soil beneath.
A cinder block foundation is a variation where the blocks are made using cinder, a byproduct of burning coal. These blocks are lighter than solid concrete blocks but still provide significant support. Cinder blocks have been widely used in construction due to their affordability and ease of handling. Concrete blocks and cinder blocks are used for both above-grade and below-grade applications, such as in basement walls or shed foundations.
The foundation itself may include concrete footing blocks at the base, ensuring the wall system has proper support and preventing shifting. Stem walls are often incorporated into block foundations, especially for homes with basements, to help create the required height and ensure better stability and durability.
Much like an RJ45 wiring diagram, which defines the connections in a network setup, understanding the components of a block foundation—from the concrete blocks to the footing blocks—helps ensure a strong and efficient base for your building.
Types of Block Foundations
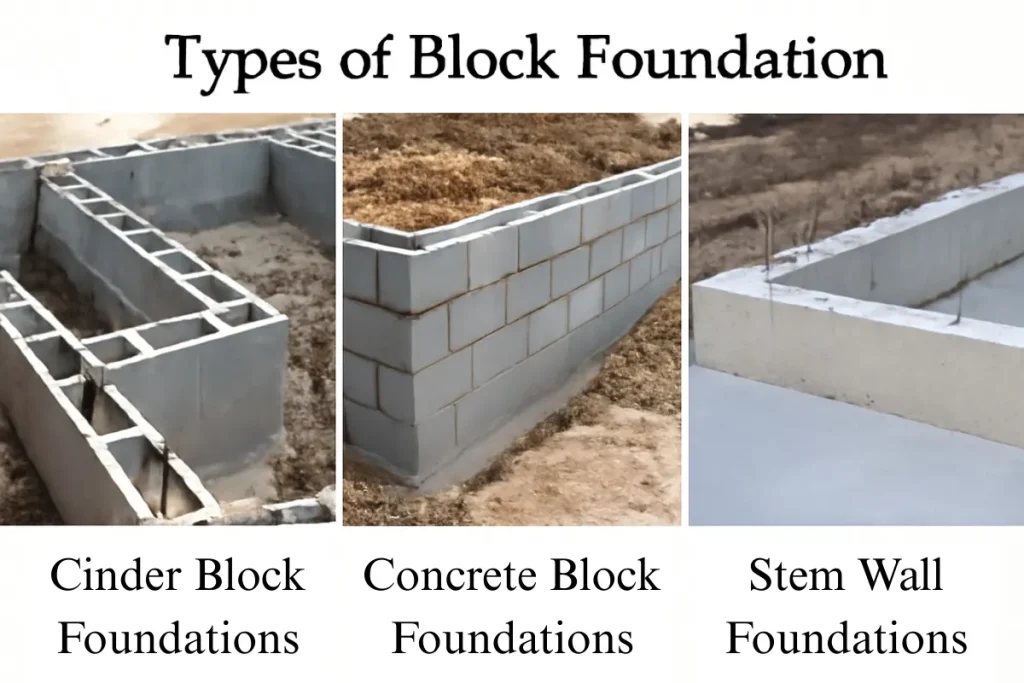
There are several types of block foundations used in construction, each serving different purposes depending on the project and site requirements. The most common types include cinder block foundations, concrete block foundations, and stem wall foundations.
- Cinder Block Foundations: Often used in residential construction, cinder block foundations are made from cinder and cement. These blocks are lighter than their concrete counterparts and offer a cost-effective solution for foundation building. They are ideal for shed foundations, perimeter walls, and crawl spaces.
- Concrete Block Foundations: Made from solid concrete blocks, this type of foundation is stronger and more durable than cinder blocks. Concrete block foundations are commonly used in basements and for homes built in areas with high moisture levels. The strength of concrete blocks helps resist shifting and settling.
- Stem Wall Foundations: A stem wall foundation involves a raised wall structure that provides an elevated foundation, typically used in homes with basements or those built on uneven ground. The stem wall is often constructed with concrete blocks or cinder blocks, and it is used to support the foundation slab or poured concrete basement walls. Stem wall details help define the height and stability of the foundation.
Each type of block foundation has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific needs of the home or building, such as cost, durability, and the site’s environmental conditions.
Advantages of Block Foundations

Block foundations offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for many construction projects:
- Cost-Effective: One of the main benefits of using block foundations is the cost. Concrete blocks and cinder blocks are generally less expensive than poured concrete foundations, making them an attractive option for homeowners and builders on a budget.
- Durability: Concrete blocks and cinder blocks are durable and can withstand significant weight and stress. Cinder block foundations are particularly resistant to moisture, and with proper installation, they can last for many years without significant wear or damage.
- Easier Repairs: Unlike poured concrete foundations, which can be difficult and expensive to repair if cracks or leaks occur, block foundations are easier to fix. You can replace individual blocks or sections as needed, which helps maintain the foundation’s integrity over time.
- Moisture Resistance: Concrete blocks are less likely to absorb water compared to other materials, which is essential in areas prone to moisture and damp conditions. Proper installation of a block foundation with the correct concrete footing blocks can prevent water damage, making them ideal for basement walls.
- Energy Efficiency: Homes built with concrete block foundations are often more energy-efficient, as the material helps regulate indoor temperatures. The mass of concrete blocks and cinder blocks can help reduce heating and cooling costs.
Just as in the world of NFT art, where digital assets are becoming a popular investment, the construction of block foundations provides a tangible, cost-effective alternative to other types of foundations in the real estate sector.
Disadvantages of Block Foundations

While block foundations offer many advantages, there are a few potential drawbacks to consider:
- Susceptibility to Cracking: Over time, concrete blocks and cinder blocks may develop cracks due to settling, ground movement, or temperature changes. Although block foundations are generally durable, cracks in the walls or between the blocks can lead to structural issues. Cinder blocks may also have weaker structural integrity compared to solid concrete blocks, making them more prone to cracking.
- Water Penetration: Although block foundations are generally resistant to moisture, they can still be vulnerable to water seepage, especially if the installation is not done correctly. Without proper drainage, water can infiltrate through the gaps between blocks or cinder blocks, potentially leading to water damage or mold growth in basements or crawl spaces. Proper waterproofing of concrete and drainage systems is essential to prevent these issues.
- Installation Challenges: While block foundations are often more affordable and easier to install than poured concrete foundations, they do require careful attention to detail. Improper installation can lead to misalignment, poor drainage, and foundation instability. Additionally, the construction of stem walls and footings can require a skilled contractor to ensure the foundation is level and properly supported.
- Maintenance: Although block foundations are easier to repair than poured concrete, they still require regular maintenance. Cracks, settling, or damage to the foundation blocks may need to be repaired over time to maintain the integrity of the structure.
Similar to the financial risks associated with certain investments, the long-term durability of foundations can be impacted by various factors, including moisture exposure and soil movement, which may increase the probability of default on a foundation’s structural integrity.
What is a Poured Concrete Foundation?

A poured concrete foundation involves the use of liquid concrete that is poured into a mold or form to create a solid, seamless base for a building. Unlike block foundations, which are made from pre-cast concrete blocks or cinder blocks, a poured concrete foundation is one continuous mass that is typically used for both basement walls and slabs.
The process involves pouring concrete into footing forms or foundation molds, where it is allowed to harden and cure. This results in a smooth, uniform foundation that offers greater strength and stability compared to block foundations. Poured concrete walls are highly resistant to moisture and offer superior durability, making them a preferred choice for homes built in areas prone to flooding or soil movement.
While poured concrete foundations tend to be more expensive than block foundations, their monolithic design helps reduce the risk of cracks and water infiltration. They are particularly effective in preventing water damage to concrete walls in basements. Poured concrete walls are also beneficial for larger or multi-story buildings, providing excellent structural integrity for the long term.
In the same way, GTM meaning helps clarify marketing strategies and tools; understanding the nuances of poured concrete foundations helps builders and homeowners make informed decisions about foundation types.
Advantages of Poured Concrete Foundations

Poured concrete foundations offer several distinct advantages over block foundations:
- Stronger Structural Integrity: Poured concrete foundations are solid, monolithic structures that are far less likely to crack or shift compared to block foundations. The seamless nature of poured concrete provides superior strength, making it ideal for multi-story buildings and basements. Poured concrete walls have fewer points of weakness compared to the joints in block foundations, which helps to maintain long-term stability.
- Better Water Resistance: Poured concrete foundations are highly resistant to water penetration due to their continuous, seamless structure. Unlike block foundations, where water can seep through the joints between blocks or cinder blocks, poured concrete walls provide an extra layer of protection against water damage. This is especially important for poured basement walls, where moisture control is crucial to preventing mold and mildew.
- Faster Construction Time: Poured concrete is faster to install compared to block foundations, as it requires fewer individual steps. The concrete is poured in a single process, reducing labor time. This makes poured concrete foundations a quicker solution for those looking to complete their construction project on time.
- Increased Durability and Longevity: Poured concrete foundations are known for their durability, offering a lifespan of several decades with minimal maintenance. They are ideal for locations with extreme weather conditions, such as areas prone to flooding, earthquakes, or freeze-thaw cycles.
Just as AI art styles have revolutionized digital creativity, poured concrete foundations provide a modern, innovative approach to building foundations that is more durable and resistant to environmental factors.
Disadvantages of Poured Concrete Foundations
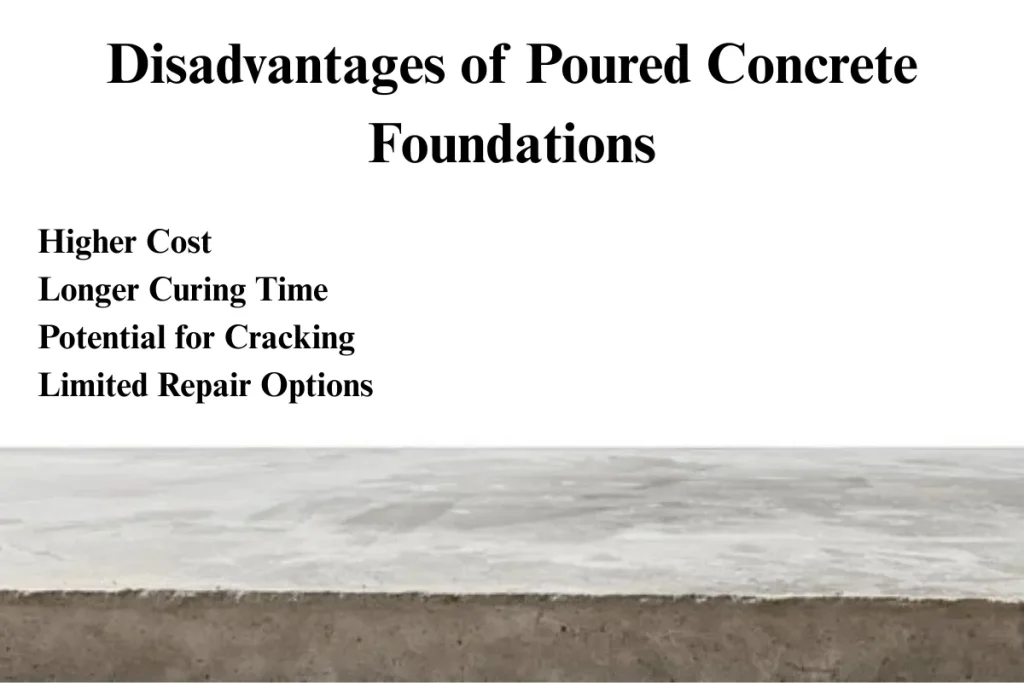
Despite the advantages, poured concrete foundations come with certain drawbacks:
- Higher Cost: One of the major disadvantages of poured concrete foundations is their cost. The materials, labor, and equipment required for pouring concrete tend to make the overall cost higher compared to block foundations. The complexity of the installation, including the need for molds, forms, and concrete delivery, adds to the expense.
- Longer Curing Time: After concrete is poured, it requires time to cure and harden, typically several days to a week, depending on weather conditions. This curing time can delay the overall construction process, making it less efficient in urgent projects. In contrast, block foundations can be installed and adjusted more quickly.
- Potential for Cracking: While poured concrete foundations are stronger than block foundations, they are not entirely immune to cracking. Changes in temperature, soil settlement, and other environmental factors can lead to cracks in the foundation. Repairing poured concrete foundations is also more complicated and costly than fixing block foundations.
- Limited Repair Options: Once poured concrete walls develop cracks or other issues, repairing them is often more difficult and expensive compared to fixing issues in block foundations. With block foundations, individual blocks can be replaced or repaired, whereas poured concrete requires patching and sometimes re-pouring sections of the foundation.
Installation of Block Foundations: DIY vs. Professional

The installation of block foundations can be handled in two ways: DIY (Do It Yourself) or by hiring professional contractors. While both options are feasible, it’s essential to understand the pros and cons of each approach before deciding.
1. DIY Block Foundation:
Installing a block foundation on your own can be a cost-effective solution if you have the necessary skills and tools. It typically involves digging the foundation trench, laying concrete footing blocks, and stacking the cinder blocks or concrete blocks to create the walls.
The process also includes ensuring proper drainage and waterproofing. For smaller projects like shed foundations or crawl spaces, DIY installation may be a viable option. However, it requires precise work to avoid issues such as misalignment, uneven settlement, and water infiltration.
2. Professional Installation:
Hiring a masonry professional or contractor for block foundation installation ensures the work is done according to industry standards. Professionals have the experience to properly install concrete footing blocks, set up stem walls, and ensure proper drainage to prevent water damage.
They also have access to heavy equipment that may be necessary for digging and laying the concrete blocks. Professional contractors are well-equipped to handle large projects like poured basement walls and foundation footings, ensuring that your foundation is level, durable, and stable.
3. Cost Considerations:
DIY installation can significantly lower the overall cost, especially for small projects. However, the potential for costly mistakes in the future may outweigh the initial savings. Professional installation typically involves higher upfront costs, but it can save you from long-term repair expenses, especially if you’re building on uneven or difficult terrain.
In conclusion, while DIY may be suitable for smaller, less complex projects, professional installation is often recommended for larger foundations or those requiring high structural integrity.
When considering installation methods, it’s essential to understand the connections in the process—similar to daisy chaining in networking, where components are linked together in a series. Professional installation ensures that each part of the foundation is properly connected and supported.
Block Foundations vs Poured Concrete Foundations
When deciding between block foundations and poured concrete foundations, several factors must be considered, including cost, durability, and the specific needs of the project.
1. Cost:
Block foundations are typically more cost-effective than poured concrete foundations. Concrete blocks and cinder blocks are less expensive to produce and install. The labor involved in laying block foundations is generally less complex, which helps reduce costs. In contrast, poured concrete foundations require a higher initial investment, as the materials, equipment, and labor involved in pouring concrete are more expensive.
2. Durability:
Poured concrete foundations are known for their strength and durability. Being a continuous, monolithic structure, poured concrete has fewer potential weak points, making it more resistant to cracks, moisture penetration, and shifting. On the other hand, block foundations are made up of individual concrete blocks or cinder blocks that are stacked together. Over time, these joints can weaken, and water may seep through if not properly sealed.
3. Water Resistance:
Poured concrete foundations have superior water resistance due to their seamless design. Block foundations, however, are more prone to water infiltration through the joints between the blocks. If waterproofing is not properly applied, cinder basement walls or block foundations may experience issues with moisture buildup, which can lead to mold and damage.
4. Installation Time:
Block foundations are faster to install, especially for smaller projects like shed foundations or crawl spaces. They are easier to handle and require less setup compared to poured concrete, which requires waiting for the concrete to cure. However, poured concrete foundations are faster for larger projects, such as poured basement walls, as they can be poured in one continuous flow.
In summary, poured concrete foundations provide a more durable and water-resistant option, while block foundations offer a more affordable and quicker solution for smaller projects or areas with less moisture exposure.
Understanding the demarcation point between block foundations and poured concrete foundations is crucial for homeowners deciding which foundation type suits their needs, as each has its own set of advantages and specific installation processes.
How to Prevent Leaks and Cracks in Your Block Foundation

Preventing leaks and cracks in a block foundation is essential to maintaining its integrity and avoiding costly repairs. Here are some key steps to protect your foundation:
- Proper Drainage: Ensuring proper drainage around the foundation is crucial. Install drainage systems like French drains or weeping tiles to channel water away from the foundation and prevent water damage to concrete walls. This will help protect cinder basement walls and block foundations from moisture buildup.
- Waterproofing: Apply a waterproofing concrete membrane on the exterior walls of the foundation. This helps create a barrier that prevents water from seeping through the concrete blocks or cinder blocks.
- Seal Joints and Cracks: Regularly inspect the joints between the concrete blocks and seal any cracks that may appear. Use masonry sealant to fill gaps and prevent water infiltration.
By taking these preventative measures, you can extend the lifespan of your block foundation and keep it in top condition.
Common Problems with Block Foundations

While block foundations are durable, they can still encounter several issues that homeowners should be aware of:
- Cracks in the Blocks: Over time, concrete blocks or cinder blocks may develop cracks due to settling or moisture exposure. These cracks can weaken the foundation and compromise its structural integrity.
- Water Seepage: If the foundation isn’t properly sealed, water can seep through the block foundation and cause damage. This is especially common in cinder basement walls, where the material is more porous.
- Shifting or Settling: If the foundation footing blocks are not properly installed or if the soil beneath the foundation shifts, the entire structure can settle unevenly, leading to cracks or misalignment in the block walls.
Regular inspection and maintenance can help address these issues early on and prevent major foundation problems down the road.
Concrete Footing Blocks and Stem Wall Construction

Concrete footing blocks and stem wall construction are crucial components of a sturdy block foundation. Here’s how they work:
- Concrete Footing Blocks: These are specially designed blocks that provide a stable base for the entire foundation. Concrete footing blocks are placed at the bottom of the foundation trench, spreading the weight of the structure evenly across the soil. They help prevent shifting and settling over time.
- Stem Wall Construction: A stem wall is a vertical structure that extends from the footing to the surface level. It helps elevate the foundation, providing support for basement walls, crawl spaces, or slabs. Stem wall foundations are often made using concrete blocks or cinder blocks. The stem wall detail typically includes reinforced steel bars to add strength to the foundation.
- Perimeter Walls and Beam: A strong perimeter wall is necessary to contain the foundation and support the load of the building. Stem walls provide the additional height needed for these perimeter walls, ensuring the foundation is properly reinforced.
By combining concrete footing blocks with stem wall construction, builders create a solid foundation that can support the structure for many years, even in areas with poor soil conditions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right foundation for your home is a crucial decision that can affect the long-term stability and durability of your property. Block foundations, whether made of cinder blocks or concrete blocks, offer a cost-effective and durable solution for many construction projects. However, they require proper installation, drainage, and maintenance to avoid issues like water infiltration and cracking.
On the other hand, poured concrete foundations provide enhanced strength and water resistance, making them ideal for homes in high-moisture areas or those needing additional structural support. While they come with a higher upfront cost and longer curing times, they offer a seamless, long-lasting foundation.
Ultimately, the choice between block foundations and poured concrete depends on factors such as budget, site conditions, and intended use. Consulting with a foundation expert can help you make the best choice for your home and ensure a strong, lasting foundation for years to come.
FAQs
Should you buy a house with a block foundation?
Buying a house with a block foundation can be a good option, but it’s important to check for any issues like cracks or water damage. Properly maintained block foundations can last for many years.
Is a block foundation cheaper than concrete?
Yes, block foundations are generally cheaper than poured concrete foundations due to lower material and labor costs.
What are the cons of block foundation?
The main cons include potential for water seepage, cracks over time, and the need for regular maintenance. Cinder blocks are also more prone to damage than concrete blocks.
Are block foundations good or bad?
Block foundations are a reliable and cost-effective option, but they require proper installation and maintenance to prevent problems like water leaks and cracking.
How long do block foundations last?
With proper maintenance, block foundations can last 50-100 years or more, depending on the material used and environmental conditions.
What is a block foundation made of?
A block foundation is typically made from concrete blocks or cinder blocks, which are made of cement and aggregates, providing a solid foundation for a building.
Is a block foundation cheaper than poured?
Yes, block foundations are generally cheaper than poured concrete foundations because they require less labor and materials.
Are cinder blocks the same as concrete blocks?
No, cinder blocks are made from cinder and cement, making them lighter than concrete blocks, which are made from solid concrete and are more durable.